Difference between revisions of "DELTA robot/zh-hans"
(Created page with "{{Languages}} = DELTA robot model = The DELTA robot is a four – degrees of freedom parallel robot of the following configuration: <center>Image:AXY;DeltaPatent.png</c...") |
(BackToTop button) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Languages}} | + | {{Languages|DELTA_robot}} |
| − | = | + | <div id="BackToTop" class="noprint" style="background-color:; position:fixed; bottom:32px; left:95%; z-index:9999; padding:0; margin:0;"> |
| + | <span style="color:blue; font-size:8pt; font-face:verdana,sans-serif; border:0.2em outset:#ceebf7; padding:0.1em; font-weight:bolder; -moz-border-radius:8px; "> | ||
| + | [[Image:TOP2.png|50px|link=#top]] </span></div> | ||
| + | = DELTA机器人模型 = | ||
| − | + | DELTA机器人是以下配置的四自由度并联机器人: | |
| Line 8: | Line 11: | ||
| − | + | Delta并联机器人设计背后的基本思想是使用平行四边形。平行四边形允许输出链路相对于输入链路保持固定的方向。 使用三个这样的平行四边形完全限制了仅具有三个纯平移自由度的移动平台的方向。 三个平行四边形的输入链路通过旋转接头安装在旋转杆上。 旋转杆的旋转接头以两种不同的方式启动:带旋转电机或线性执行器。 最后,第四条连杆用于将旋转运动从基座传递到安装在移动平台上的末端执行器。 | |
| − | + | WIPO专利于1987年6月18日发布([http://www.delphion.com/details?&pn10=WO08703528 WO 87/03528]): | |
| − | '' | + | ''“该装置包括基座元件(1)和可动元件(8)。 三个控制臂(4)在其第一末端(15)处刚性地安装在可以旋转的三个轴(2)上。 由轴(2)和臂(4)形成的三个组件是三个致动器(13)的可移动部分,其中固定部分(3)与基部元件成一体。 每个控制臂的另一端(16)通过一方面铰接安装到控制臂的第二端(16)的两个连接杆(5a,5b)与可动元件整体形成,另一方面, 到可移动元件。 无论三个控制臂的运动如何,可移动元件的空间中的倾斜度和取向保持不变。 可移动元件支撑工作元件(9),其中旋转由位于基座元件上的固定电动机(11)控制。 伸缩臂(14)将电机连接到工作元件。”'' |
| − | + | 同样: ([http://www.delphion.com/details?&pn10=US04976582 US 4,976,582]),和 ([http://www.delphion.com/details?pn=EP00250470B1 EP 0 250 470]). | |
<center>[[Image:AXY;ABBDelta.png]]</center> | <center>[[Image:AXY;ABBDelta.png]]</center> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
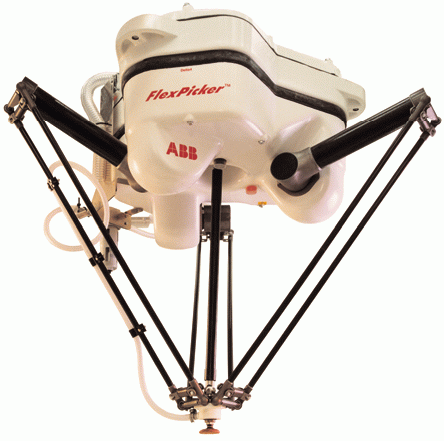
<center>ABB Flexible Automation's IRB 340 FlexPicker</center> | <center>ABB Flexible Automation's IRB 340 FlexPicker</center> | ||
| − | == | + | == DELTA工作空间 == |
[[Image:AXY;DeltaWspace.png ]] | [[Image:AXY;DeltaWspace.png ]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 33: | ||
| − | + | Delta运动学与'''XYZR'''机器人类型(X,Y,Z和Roll)的点一起使用,其中前三个坐标始终以毫米表示,旋转角度以度为单位。 | |
| + | DELTA WORLD工作区受关节限制和以下辅助笛卡尔边界的限制,可供用户使用: | ||
| − | + | * RMAX – 笛卡尔点的最大半径 (<math> \sqrt {x^2 + y^2 + z^2} </math>), 不允许超出该半径的点。 | |
| − | + | * RMIN - 笛卡尔点的最小半径 (<math> \sqrt {x^2 + y^2 + z^2} </math>). 该半径内不允许有点。 | |
| − | * RMAX – | + | * ZMIN – “最低”机器人位置的'''z'''坐标。该平面以下的任何点都不允许。 |
| − | * RMIN - | ||
| − | * ZMIN – '''z''' | ||
[[Image:AXY;DeltaKinematics1.png]] | [[Image:AXY;DeltaKinematics1.png]] | ||
| − | == | + | == 机器人配置 == |
| − | + | Delta机器人没有配置标志,有一个独特的逆运动学解决方案。这进一步意味着逆运动学函数'''ToJoint'''中的配置参数对结果没有影响。同样像MOVES,CIRCLE或PASS THROUGH这样的笛卡尔运动不会被任何命令配置标志(acmd,ecmd,wcmd)影响,这些运动将独立于任何这些标志的值。 | |
| − | == | + | == 奇异点 == |
| − | + | Delta机器人与开式运动学连杆机器人相反,没有单个关节位置,其中关节速度趋于无穷大,被称为谓的“直接运动学奇点”,其中机器人的刚度显着降低。 | |
| Line 52: | Line 54: | ||
| − | + | 当上臂连杆彼此平行时的情况。 在这种奇异配置下,机械臂不能抵抗施加在移动平台平面上的任何力。 | |
| − | |||
| − | + | 在我们这种情况下更为'''理论'''的另一个奇异的位置就是所谓的直接运动学奇异结构,其中所有的上臂连接在移动平台的平面内。在这种构造下,机械臂执行机构不能抵抗在z方向上施加到移动平台的任何力。 | |
| − | ''' | + | '''这种情况只有在<math>L_1 +R_{big} >= L_2 + R_{small} </math> 才能实现!''' |
| − | == | + | == DELTA机器人的几何参数 == |
[[File:DELTAGEOMETRY.PNG]] | [[File:DELTAGEOMETRY.PNG]] | ||
| − | + | 对于DELTA系列机器人有: | |
{| style="border-spacing:0;" | {| style="border-spacing:0;" | ||
| − | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center> | + | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center>参数</center> |
| − | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center>MC- | + | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center>MC-Basic属性名称</center> |
| − | | style="border:0.0069in solid #000000;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center> | + | | style="border:0.0069in solid #000000;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center>值(mm)</center> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 98: | Line 99: | ||
| − | + | 机器人的'''连杆'''矩阵属性的上述参数必须填写在机器人的设置文件中。为了使系统接受上述设置,必须执行“'''configgroup'''”命令。该模型假设三个基本电机旋转正好120度。也假设所有三个连杆都具有相同的尺寸。WORLD坐标系位于电机平面的中心。 请注意,只有上述参数集才会影响机器人几何形状。'''''<nowiki>link[][]</nowiki>'''''和 '''''<nowiki>axis[][] </nowiki>'''''的其余部分不会以任何方式影响机器人几何形状,并且不受'''configgroup''' 命令或任何机器人命令的影响。 | |
| − | == | + | == 典型DELTA姿态 == |
| − | + | 最远(最高)可达的Z坐标和最大关节角度。 | |
[[File:DELTAPOS1.PNG]] | [[File:DELTAPOS1.PNG]] | ||
| Line 111: | Line 112: | ||
| − | + | 最近(最低)可达的Z坐标和最大关节角度。 | |
[[File:DELTAPOS2.PNG]] | [[File:DELTAPOS2.PNG]] | ||
| − | + | 如果<math>L_1 + R_{big} >= L_2 + R_{small} </math>则以下是正确的'''(不适用于我们的情况)''': | |
<math>Z_{min} = \sqrt {L_1^2 - (L_2 + R_{small}-R_{big})^2}</math> | <math>Z_{min} = \sqrt {L_1^2 - (L_2 + R_{small}-R_{big})^2}</math> | ||
| Line 126: | Line 127: | ||
| − | + | “零”位置, 对<math> \theta = 0 </math> | |
| Line 135: | Line 136: | ||
| − | + | 具有以下几何形状的机器人: | |
{| style="border-spacing:0;" | {| style="border-spacing:0;" | ||
| − | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center> | + | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center>参数</center> |
| − | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center> | + | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| <center>值(mm)</center> |
| style="border-top:none;border-bottom:none;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| | | style="border-top:none;border-bottom:none;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| | ||
| style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| | | style="border-top:0.0069in solid #000000;border-bottom:0.0069in solid #000000;border-left:0.0069in solid #000000;border-right:none;padding-top:0in;padding-bottom:0in;padding-left:0.075in;padding-right:0.075in;"| | ||
| Line 188: | Line 189: | ||
--> | --> | ||
| − | == | + | == 姿态角 == |
| − | + | DELTA运动学只有一个由第四个电机直接驱动的(一对一)姿态角(滚动)。WORLD旋转角度的值始终等于在[-180,180]角度值之间的第四关节位置(围绕)。姿态插值由OrientationFollwing标志决定。在DELTA机器人的情况下,关节和世界角度是直接相关的,因此我们只有两个选项的OrientationFollowing标志:</nowiki> | |
| − | * | + | * 在最初和最终旋转角度之间采取更长的路径: '''OrientationFollowing标志等于2或3''' |
| − | * | + | * 在初始和最终旋转角度之间采取较短的路径: '''OrientationFollowing标志等于0或1''' |
Latest revision as of 06:14, 10 August 2017
| 语言: | English • 中文(简体) |
|---|
DELTA机器人模型
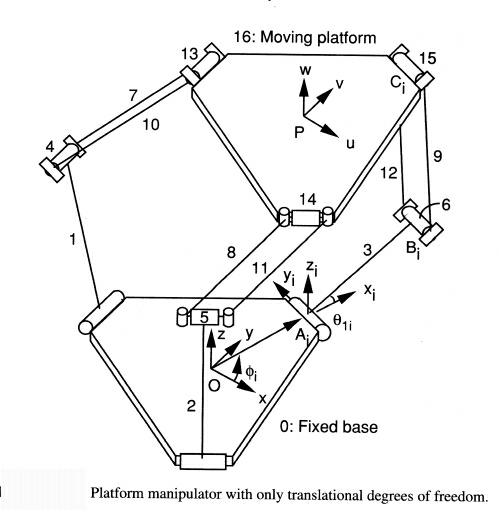
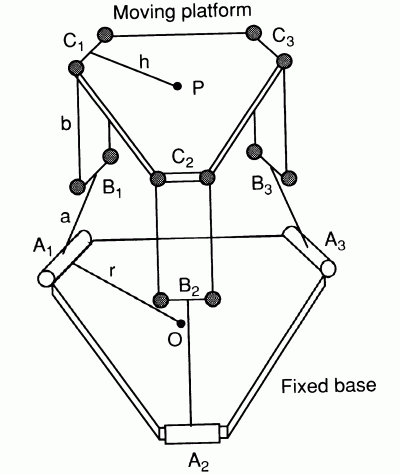
DELTA机器人是以下配置的四自由度并联机器人:
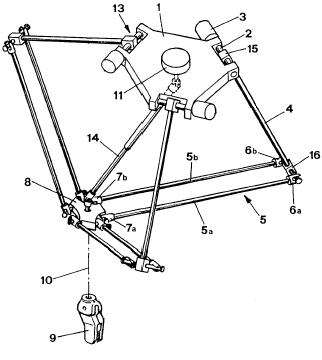
Delta并联机器人设计背后的基本思想是使用平行四边形。平行四边形允许输出链路相对于输入链路保持固定的方向。 使用三个这样的平行四边形完全限制了仅具有三个纯平移自由度的移动平台的方向。 三个平行四边形的输入链路通过旋转接头安装在旋转杆上。 旋转杆的旋转接头以两种不同的方式启动:带旋转电机或线性执行器。 最后,第四条连杆用于将旋转运动从基座传递到安装在移动平台上的末端执行器。
WIPO专利于1987年6月18日发布(WO 87/03528):
“该装置包括基座元件(1)和可动元件(8)。 三个控制臂(4)在其第一末端(15)处刚性地安装在可以旋转的三个轴(2)上。 由轴(2)和臂(4)形成的三个组件是三个致动器(13)的可移动部分,其中固定部分(3)与基部元件成一体。 每个控制臂的另一端(16)通过一方面铰接安装到控制臂的第二端(16)的两个连接杆(5a,5b)与可动元件整体形成,另一方面, 到可移动元件。 无论三个控制臂的运动如何,可移动元件的空间中的倾斜度和取向保持不变。 可移动元件支撑工作元件(9),其中旋转由位于基座元件上的固定电动机(11)控制。 伸缩臂(14)将电机连接到工作元件。”
同样: (US 4,976,582),和 (EP 0 250 470).
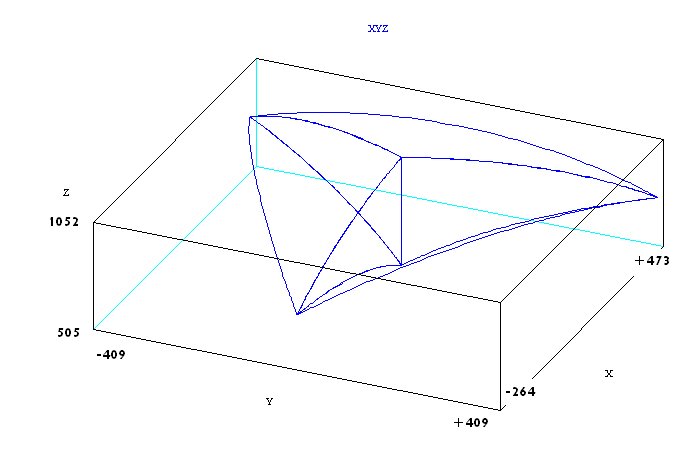
DELTA工作空间
Delta运动学与XYZR机器人类型(X,Y,Z和Roll)的点一起使用,其中前三个坐标始终以毫米表示,旋转角度以度为单位。
DELTA WORLD工作区受关节限制和以下辅助笛卡尔边界的限制,可供用户使用:
- RMAX – 笛卡尔点的最大半径 (), 不允许超出该半径的点。
- RMIN - 笛卡尔点的最小半径 (). 该半径内不允许有点。
- ZMIN – “最低”机器人位置的z坐标。该平面以下的任何点都不允许。
机器人配置
Delta机器人没有配置标志,有一个独特的逆运动学解决方案。这进一步意味着逆运动学函数ToJoint中的配置参数对结果没有影响。同样像MOVES,CIRCLE或PASS THROUGH这样的笛卡尔运动不会被任何命令配置标志(acmd,ecmd,wcmd)影响,这些运动将独立于任何这些标志的值。
奇异点
Delta机器人与开式运动学连杆机器人相反,没有单个关节位置,其中关节速度趋于无穷大,被称为谓的“直接运动学奇点”,其中机器人的刚度显着降低。
当上臂连杆彼此平行时的情况。 在这种奇异配置下,机械臂不能抵抗施加在移动平台平面上的任何力。
在我们这种情况下更为理论的另一个奇异的位置就是所谓的直接运动学奇异结构,其中所有的上臂连接在移动平台的平面内。在这种构造下,机械臂执行机构不能抵抗在z方向上施加到移动平台的任何力。
这种情况只有在 才能实现!
DELTA机器人的几何参数
对于DELTA系列机器人有:
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
机器人的连杆矩阵属性的上述参数必须填写在机器人的设置文件中。为了使系统接受上述设置,必须执行“configgroup”命令。该模型假设三个基本电机旋转正好120度。也假设所有三个连杆都具有相同的尺寸。WORLD坐标系位于电机平面的中心。 请注意,只有上述参数集才会影响机器人几何形状。link[][]和 axis[][] 的其余部分不会以任何方式影响机器人几何形状,并且不受configgroup 命令或任何机器人命令的影响。
典型DELTA姿态
最远(最高)可达的Z坐标和最大关节角度。
最近(最低)可达的Z坐标和最大关节角度。
如果则以下是正确的(不适用于我们的情况):
“零”位置, 对
具有以下几何形状的机器人:
| |
|
|||
| |
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|
Test:
-->?ToCart({0,0,0,0})
#{-5.68434e-14 , 0 , 505.569 , 0}
-->?toCart({106.87,106.87,106.87,0})
#{-7.10543e-15 , 0 , 1052.43 , 0}
-->
姿态角
DELTA运动学只有一个由第四个电机直接驱动的(一对一)姿态角(滚动)。WORLD旋转角度的值始终等于在[-180,180]角度值之间的第四关节位置(围绕)。姿态插值由OrientationFollwing标志决定。在DELTA机器人的情况下,关节和世界角度是直接相关的,因此我们只有两个选项的OrientationFollowing标志:</nowiki>
- 在最初和最终旋转角度之间采取更长的路径: OrientationFollowing标志等于2或3
- 在初始和最终旋转角度之间采取较短的路径: OrientationFollowing标志等于0或1