Difference between revisions of "Time Based Profile (Trapezoidal Acceleration)/zh-hans"
(AXY: new links) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Languages}} | + | {{Languages|Time_Based_Profile_(Trapezoidal_Acceleration)}} |
= 概述 = | = 概述 = | ||
<font color="red"> | <font color="red"> | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</font> | </font> | ||
| − | + | 两个分析器基本上都是在路径生成期间改变状态的状态机,并且基于每个状态使用不同的公式来计算分析器输出(位置,速度,加速度)。 这些状态是:加速度增加,加速度饱和,加速度减小,零加速度。可以在运动期间重复一些状态(例如,加速状态,然后是减速状态),并且可以完全省略一些状态(例如,在短暂运动中为零加速)。<br> | |
| − | + | 这两个分析器之间的主要区别是状态选择算法,即系统从一个状态切换到另一个状态的条件。当前的实现(自版本4.5.25起的固件)主要以速度为基础。这意味着当前速度值是分析器切换到另一状态的主要标准。然而,速度值还不够,因此还要使用附加的内部变量:相位角,目标距离,分析器状态。 | |
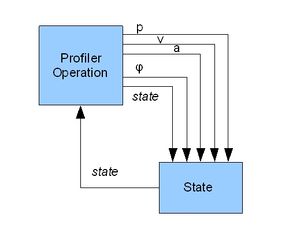
[[Image:AXY-Velocity Based profiler.jpg|thumb|''Illustration 1: Velocity Based Profiler'']] | [[Image:AXY-Velocity Based profiler.jpg|thumb|''Illustration 1: Velocity Based Profiler'']] | ||
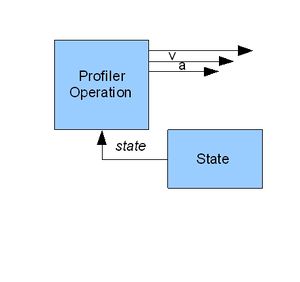
[[Image:AXY-Time Based Profiler.jpg|thumb|''Illustration 2: Time Based Profiler'']] | [[Image:AXY-Time Based Profiler.jpg|thumb|''Illustration 2: Time Based Profiler'']] | ||
| − | + | 新的分析器(自版本4.5.25起)具有仅基于一个变量(当前时间)的状态变化条件。 离线预计算(这两个分析器都是共同的)将预先计算每个状态的切换时间,这将在状态改变时给出一个简单的条件。 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | 这种方法比基于速度的分析器提供了一些好处。 其中之一是采用[[Safe Superposition (SP) blending| safe SP blending feature.]] | ||
{| class="prettytable" border = 1 | {| class="prettytable" border = 1 | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | 基于时间的分析器 |
| − | | | + | | 基于速度的分析器 |
|- | |- | ||
| RTK load | | RTK load | ||
| − | | | + | | 非常小,因为没有检查制动距离 |
| − | | | + | | 在每个采样中检查制动距离。 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 时间离散化 - 样本落在不同阶段之间 |
| − | | | + | | 无,因为(p,v,a)值仅在当前时间值上计算 |
| − | | | + | | 我们需要分别计算每个阶段,然后减去 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 轻松在线改变目标点 |
| − | | | + | | 需要全部重复预计算 |
| − | | | + | | 由于制动距离总是被检查,所以它相对来说比较麻烦。 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 时间驱动事件(即,在特定时间实例(在达到目标点之前)定义事件) |
| − | | | + | | 一个简单的内置功能 |
| − | | | + | | 非常不便于实施,因为我们实际上不知道运动的总执行时间 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 总执行时间的预测(例如,在SP混合中,防止第二运动在第二次完成之前进入) |
| − | | | + | | 一个简单的内置功能 |
| − | | | + | | 非常不便于实施,因为我们实际上不知道运动的总执行时间 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | = | + | = 实施细则 = |
| − | == | + | == 语言接口 == |
| − | + | 系统原本只支持两种类型的运动曲线:正弦加速度(SA)和梯形加速度(TV)。用户通过定义平滑因子选择运动曲线:0 - TV,其他一切都是SA配置文件。这是非常直观的,因为梯形加速度(TV)是用户可以选择的最不平滑的配置文件(种类简单)。但是,这对于定义其他配置文件类型非常不方便。 因此引入了新的属性:<br> <ELEMENT>.[[MC-Basic:element.PROFILERTYPE| PROFILERTYPE]] | |
| − | == | + | == 分析器特性 == |
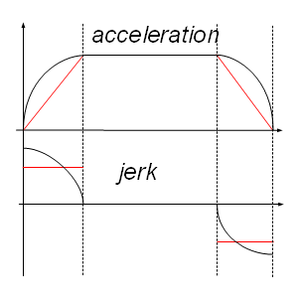
[[Image:AXY-SA vs TA jerk profile.png|thumb|''Illustration 3: SA vs TA jerk profile'']] | [[Image:AXY-SA vs TA jerk profile.png|thumb|''Illustration 3: SA vs TA jerk profile'']] | ||
| − | + | 第一个基于时间的分析器实现的是梯形加速度曲线。 基于时间的分析器提供平滑的速度和位置曲线(“S”曲线)。 与正弦加速度曲线相比,该曲线对于相同的加速度具有减小的加加速度值,并且在加速度曲线中具有一个更多的加加速度不连续点。 然而,考虑到加加速度值也大约降低了三倍(3.14倍),可以假设两个曲线基本相同。 将TA转换为TV是通过减少加速度增加时间到比运动采样时间更短来完成的,与SA轮廓相反,这种变换有时默认地进行(加速时间小于5个样品)。 在该曲线类型中,通过J / A> T保证速度平滑度。 | |
| + | [[File:AXY;Trpeze Accleration Profile.jpg|''Illustration 3: Trapezoidal Acceleration Profile'']] | ||
| − | |||
| + | === 反作用: === | ||
| − | = | + | ''所提出的轮廓(TA)不能具有'''非零的初始和/或最终速度'''。 此约束对ProfileType = 2的使用造成以下限制:<br/>'' |
| − | + | * VORD变更的执行将推迟到改变之后输入的第一个运动,即速度指令'''没有在线变化'''。 | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | * | + | * 此运动曲线不允许使用StartType'''即时或快速立即的动作'''。 |
| − | * | + | * 在SP-混和模式下,添加一个'''阻止在第二个动作完成之前进入第三个动作'''的功能将比较简单。 |
| − | * | + | * 新的分析器'''允许在运动结束之前引入时间事件。''' |
| − | * | + | * 连接(Vfinal≠0) - '''不可能''',因为这种类型的分析器不接受非零的初始和/或最终速度。<br/> |
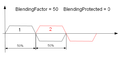
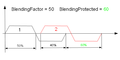
| − | * BlendingMethod = | + | * BlendingMethod= 1(连续路径)和(PrfType = 2),'''不起作用'''。 在这种情况下,混合在曲线跟随模式下完成,其中只有一个运动执行该曲线规划,而另一个运动跟随它: |
| − | * BlendingMethod = 2 (Super-Position) | + | * BlendingMethod = 2 (Super-Position)完全可操作 |
| − | * BlendingMethod = 3 (AI) | + | * BlendingMethod = 3 (AI) 功能齐全,独立于所选的分析器类型。 |
| − | = | + | = 新的混合属性 = |
| − | * [[MC-Basic: | + | * [[MC-Basic:element.CURRENTTIME| CurrentTime ]] |
| − | * [[MC-Basic: | + | * [[MC-Basic:element.TOTALTIME| TotalTime ]] |
| − | * [[MC-Basic: | + | * [[MC-Basic:element.BLENDINGSTARTCONDITION| BlendingStartCondition ]] |
| − | * [[MC-Basic: | + | * [[MC-Basic:element.BLENDPROTECTED| BlendProtected ]] |
| Line 104: | Line 101: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | = | + | = 编码问题 = |
| − | + | 基于时间的分析器将具有三个不同的功能部分,这与我们目前使用默认基于速度的分析器相同: | |
| − | * | + | * 预先计算,其中给定的速度,加速度和加加速度的用户参数被转换成实际操作值的部分。 |
| − | * | + | * 实时执行器是每个采样时间和产生下一个三个一组 ''(位置,速度,加速度) ''。 |
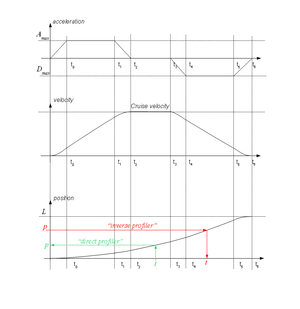
| − | * ''' | + | * '''反向分析器'''功能,根据分析器路径中给定的位置计算内部分析器参数的例程。在基于速度的轮廓中,这个功能是有意义的。在基于时间的配置文件中,这个功能要简单得多,并且将以这种形式<math>t = Profiler^{-1} (p)</math>。此功能在实现SP混合的BlendProtected功能方面至关重要。 |
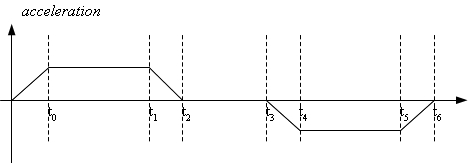
[[Image:AXY;Full Trapeze Acceleration Profile.png|thumb|''Illustration 4: Trapezoidal Acceleration Profile, possibility of "inverse profiler"'']] | [[Image:AXY;Full Trapeze Acceleration Profile.png|thumb|''Illustration 4: Trapezoidal Acceleration Profile, possibility of "inverse profiler"'']] | ||
| − | = | + | = 参见 = |
* [[Safe Superposition (SP) blending| Safe SP blending]] | * [[Safe Superposition (SP) blending| Safe SP blending]] | ||
* [[AXY:Blending| Blending Behavior]] | * [[AXY:Blending| Blending Behavior]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:25, 13 September 2017
| 语言: | English • 中文(简体) |
|---|
概述
本文档介绍了ControlStudio中的新运动分析器。 为了了解新的分析器的特性,我们首先描述当前的分析器实现。
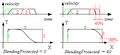
两个分析器基本上都是在路径生成期间改变状态的状态机,并且基于每个状态使用不同的公式来计算分析器输出(位置,速度,加速度)。 这些状态是:加速度增加,加速度饱和,加速度减小,零加速度。可以在运动期间重复一些状态(例如,加速状态,然后是减速状态),并且可以完全省略一些状态(例如,在短暂运动中为零加速)。
这两个分析器之间的主要区别是状态选择算法,即系统从一个状态切换到另一个状态的条件。当前的实现(自版本4.5.25起的固件)主要以速度为基础。这意味着当前速度值是分析器切换到另一状态的主要标准。然而,速度值还不够,因此还要使用附加的内部变量:相位角,目标距离,分析器状态。
新的分析器(自版本4.5.25起)具有仅基于一个变量(当前时间)的状态变化条件。 离线预计算(这两个分析器都是共同的)将预先计算每个状态的切换时间,这将在状态改变时给出一个简单的条件。
这种方法比基于速度的分析器提供了一些好处。 其中之一是采用 safe SP blending feature.
| 基于时间的分析器 | 基于速度的分析器 | |
| RTK load | 非常小,因为没有检查制动距离 | 在每个采样中检查制动距离。 |
| 时间离散化 - 样本落在不同阶段之间 | 无,因为(p,v,a)值仅在当前时间值上计算 | 我们需要分别计算每个阶段,然后减去 |
| 轻松在线改变目标点 | 需要全部重复预计算 | 由于制动距离总是被检查,所以它相对来说比较麻烦。 |
| 时间驱动事件(即,在特定时间实例(在达到目标点之前)定义事件) | 一个简单的内置功能 | 非常不便于实施,因为我们实际上不知道运动的总执行时间 |
| 总执行时间的预测(例如,在SP混合中,防止第二运动在第二次完成之前进入) | 一个简单的内置功能 | 非常不便于实施,因为我们实际上不知道运动的总执行时间 |
实施细则
语言接口
系统原本只支持两种类型的运动曲线:正弦加速度(SA)和梯形加速度(TV)。用户通过定义平滑因子选择运动曲线:0 - TV,其他一切都是SA配置文件。这是非常直观的,因为梯形加速度(TV)是用户可以选择的最不平滑的配置文件(种类简单)。但是,这对于定义其他配置文件类型非常不方便。 因此引入了新的属性:
<ELEMENT>. PROFILERTYPE
分析器特性
第一个基于时间的分析器实现的是梯形加速度曲线。 基于时间的分析器提供平滑的速度和位置曲线(“S”曲线)。 与正弦加速度曲线相比,该曲线对于相同的加速度具有减小的加加速度值,并且在加速度曲线中具有一个更多的加加速度不连续点。 然而,考虑到加加速度值也大约降低了三倍(3.14倍),可以假设两个曲线基本相同。 将TA转换为TV是通过减少加速度增加时间到比运动采样时间更短来完成的,与SA轮廓相反,这种变换有时默认地进行(加速时间小于5个样品)。 在该曲线类型中,通过J / A> T保证速度平滑度。
反作用:
所提出的轮廓(TA)不能具有非零的初始和/或最终速度。 此约束对ProfileType = 2的使用造成以下限制:
- VORD变更的执行将推迟到改变之后输入的第一个运动,即速度指令没有在线变化。
- 此运动曲线不允许使用StartType即时或快速立即的动作。
- 在SP-混和模式下,添加一个阻止在第二个动作完成之前进入第三个动作的功能将比较简单。
- 新的分析器允许在运动结束之前引入时间事件。
- 连接(Vfinal≠0) - 不可能,因为这种类型的分析器不接受非零的初始和/或最终速度。
- BlendingMethod= 1(连续路径)和(PrfType = 2),不起作用。 在这种情况下,混合在曲线跟随模式下完成,其中只有一个运动执行该曲线规划,而另一个运动跟随它:
- BlendingMethod = 2 (Super-Position)完全可操作
- BlendingMethod = 3 (AI) 功能齐全,独立于所选的分析器类型。
新的混合属性
编码问题
基于时间的分析器将具有三个不同的功能部分,这与我们目前使用默认基于速度的分析器相同:
- 预先计算,其中给定的速度,加速度和加加速度的用户参数被转换成实际操作值的部分。
- 实时执行器是每个采样时间和产生下一个三个一组 (位置,速度,加速度) 。
- 反向分析器功能,根据分析器路径中给定的位置计算内部分析器参数的例程。在基于速度的轮廓中,这个功能是有意义的。在基于时间的配置文件中,这个功能要简单得多,并且将以这种形式。此功能在实现SP混合的BlendProtected功能方面至关重要。
参见
--Mirko 08:22, 20 December 2010 (CET)