Difference between revisions of "Concatenation of Movements"
m |
(AXY: new links) |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Languages|Concatenation_of_Movements}} | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| − | Using ControlStudio, two motions can be "glued" together using a non-zero final velocity value. This method is called concatenation. It is a | + | Using ControlStudio, two motions can be "glued" together using a non-zero final velocity value. This method is called concatenation. It is a basic way of blending. Each motion is fully executed according to its interpolation specification, as opposed to blending (CP, SP or AI) where the path is modified to fit to the motion constraints. |
== Issuing Concatenation == | == Issuing Concatenation == | ||
| − | Depending if the given motion element is group/axis or robot the following final-velocity properties are used: | + | Depending if the given motion element is a group/axis or a robot, the following final-velocity properties are used: |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * '''Group/axis''': [[MC-Basic:element.VELOCITYFINAL|VFINAL]] (together with [[MC-Basic:element.VELOCITYCRUISE|VCRUISE]]). | ||
| + | * '''Robot''': [[MC-Basic:robot.VELOCITYFINALTRANS|VFTRAN]] and [[MC-Basic:robot.VELOCITYFINALROT|VFROT]] (together with [[MC-Basic:robot.VELOCITYTRANS|VTRAN]] and [[MC-Basic:robot.VELOCITYROT|VROT]]). | ||
== Special Issues == | == Special Issues == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
=== Profiling === | === Profiling === | ||
| − | * | + | * When specifying final velocity, it is important to note that the actual final velocity can differ. The system motion profiler tries to generate the best (fastest) motion profile under the given limitations. The actual final velocity will depend on the initial velocity of the movement, movement length, and all the motion limitations (e.g., acceleration/deceleration max, jerk max). |
| − | * | + | * If a series of concatenated motions is issued and the last one starts with such a high velocity that the movement cannot be stopped at the end, an '''AUTOMATIC BRAKING''' error will be issued. |
| − | * | + | * If the final velocity is too high, the highest achievable final velocity will be reached instead. |
=== Discretization === | === Discretization === | ||
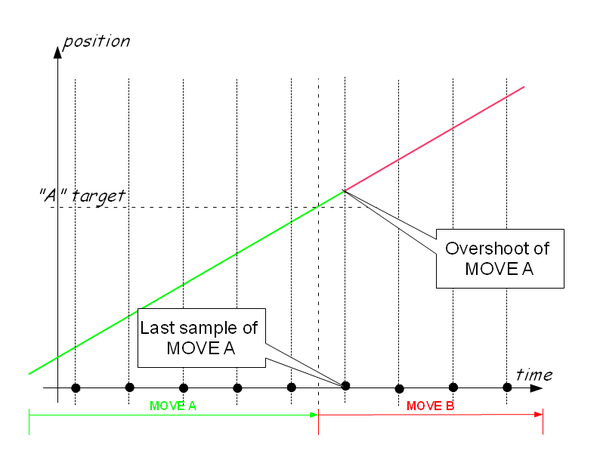
| − | Discretization is a phenomenon occurring in motion-concatenation. A movement that ends with non-zero final velocity can never exactly | + | Discretization is a phenomenon occurring in motion-concatenation. A movement that ends with a non-zero final velocity can never end exactly at the last motion sample. Since a motion profile generation is done in every system sample at a specified sample rate, the last sample will never be exact. In other words: |
| + | |||
<math>v \cdot n \cdot T \neq L </math><br> | <math>v \cdot n \cdot T \neq L </math><br> | ||
| − | The overshoot will be transferred to the next movement as its new initial position. In | + | The overshoot will be transferred to the next movement as its new initial position. In transitions between circles and lines, the appropriate projection-factor will be taken into account. |
| − | The example | + | The following example shows two movements (to A and then to B): |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
MOVE A vcruise = 100 vfinal = 100 | MOVE A vcruise = 100 vfinal = 100 | ||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Note that the second motion will start from a point that is little bit further from the point A. | |
| − | [[File:AXY;Conncatenation.png | Discretization]] | + | [[File:AXY;Conncatenation.png |600px| Discretization]] |
=== Path-PLS === | === Path-PLS === | ||
| − | + | In case of motion concatenation and PLS, the second movement will miss the PLS set at 0% as 0% actually never happens. | |
Latest revision as of 13:04, 13 September 2017
| Language: | English • 中文(简体) |
|---|
Contents
Introduction
Using ControlStudio, two motions can be "glued" together using a non-zero final velocity value. This method is called concatenation. It is a basic way of blending. Each motion is fully executed according to its interpolation specification, as opposed to blending (CP, SP or AI) where the path is modified to fit to the motion constraints.
Issuing Concatenation
Depending if the given motion element is a group/axis or a robot, the following final-velocity properties are used:
Special Issues
Profiling
- When specifying final velocity, it is important to note that the actual final velocity can differ. The system motion profiler tries to generate the best (fastest) motion profile under the given limitations. The actual final velocity will depend on the initial velocity of the movement, movement length, and all the motion limitations (e.g., acceleration/deceleration max, jerk max).
- If a series of concatenated motions is issued and the last one starts with such a high velocity that the movement cannot be stopped at the end, an AUTOMATIC BRAKING error will be issued.
- If the final velocity is too high, the highest achievable final velocity will be reached instead.
Discretization
Discretization is a phenomenon occurring in motion-concatenation. A movement that ends with a non-zero final velocity can never end exactly at the last motion sample. Since a motion profile generation is done in every system sample at a specified sample rate, the last sample will never be exact. In other words:
The overshoot will be transferred to the next movement as its new initial position. In transitions between circles and lines, the appropriate projection-factor will be taken into account.
The following example shows two movements (to A and then to B):
MOVE A vcruise = 100 vfinal = 100 MOVE B vcruise = 100
Note that the second motion will start from a point that is little bit further from the point A.
Path-PLS
In case of motion concatenation and PLS, the second movement will miss the PLS set at 0% as 0% actually never happens.