TARM robot
Contents
TARM (Traverse Arm) robot
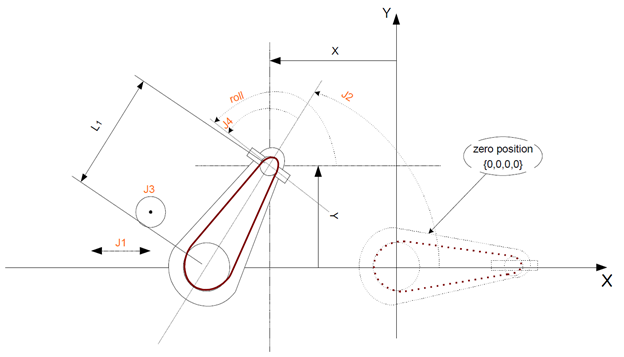
General setup
- J1 is the linear traverse axis
- J2 is angular axis of the Z-Roll couple.
- J3 linear (Z) axis of the Z-Roll couple.
- J4 additional rotational axis of the end-effector.
Kinematics
Main Kinematics Equations
Direct Kinematics:
Inverse Kinematics:
| NOTE | |
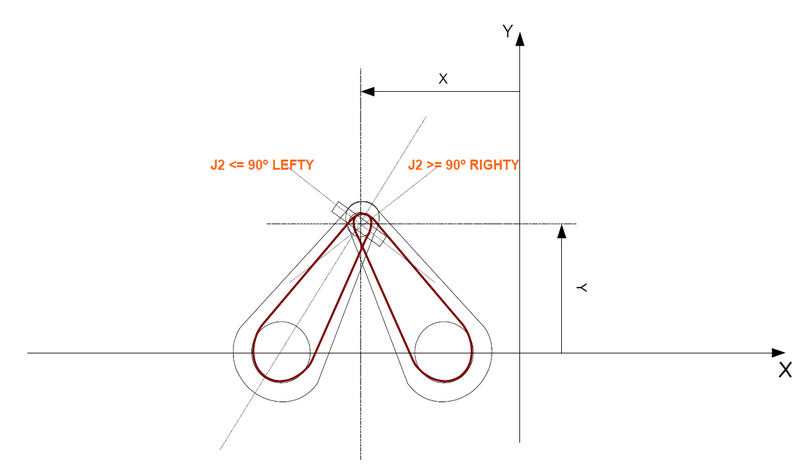
| Singularity J2 at 90 degrees! |
Additionally there is standard coupling between motor axes A2, A3 and J2, J3 (the SCARA/OCP gear box).
Robot Configuration
Reference positions
Cartesian Location Joint (LEFTY) Joint (Righty)
#{L1 , 0 , 0 , 0} {0 , 0 , 0 , 0} {2L1 , 180 , 0 , -180}
#{0 , L1 , 0 , 0}1 {0 , 90 , 0 , -90} {0 , 90 , 0 , -90}
#{-L1 , 0 , 0 , 0} {-2*L1 , 0 , 0 , 0} {0 , 180 , 0 , -180}
#{0 , 0 , 0 , 0} {-L1 , 0 , 0 , 0} {L1 , 180 , 0 , -180}
Setup file
This kinematics type is defined using “model = 7” identifier. Traverse Arm Kinematics group definition:
common shared Tarm as group axnm = a5 axnm = a6 axnm = a7 axnm = a8 model = 7
The only geometric parameter – segment length L1 is kept in <robot>.link[1][1]
|
Standard Z-Roll coupling definition (same as SCARA or OCP) |
cplg[1][1] = 1 |
|
Definition of L1 = 500 mm and positive vertical direction of Z axis. |
axis[1][1] = 0 |