Difference between revisions of "Dynamic Models"
(→Dynamic Model 1) |
(→Dynamic Model 1) |
||
| Line 244: | Line 244: | ||
Description: | Description: | ||
| − | :* <math> g </math> - | + | :* <math> g </math> - Gravity constant |
| − | :* <math> m_{i} </math> - | + | :* <math> m_{i} </math> - Mass of the i<sup>th</sup> link |
| − | :* <math> a_{i} </math> - | + | :* <math> a_{i} </math> - length of the common normal between the i<sup>th</sup> and i<sup>th+1</sup> joints |
| + | :* <math> d_{i} </math> - offset along z axis between the i<sup>th</sup> and i<sup>th+1</sup> joints | ||
:* <math> l_{i} </math> - The distance from the i<sup>th</sup> joint to the center of mass of the i<sup>th</sup> link | :* <math> l_{i} </math> - The distance from the i<sup>th</sup> joint to the center of mass of the i<sup>th</sup> link | ||
| Line 280: | Line 281: | ||
|7 | |7 | ||
|<math>I_{7} = m_{3}*l_{3,y}^2+I_{3,xx}-I_{3,yy}+m_{4}*l_{4,z}^2+2*m_{4}*d_{4}*l_{4,z}+(m_{4}+m_{5}+m_{6})*(d_{4}^2-a_{3}^2)+I_{4,yy}-I_{4,yy}+I_{5,zz}-I_{5,yy}+m_{6}*l_{6,z}^2-I_{6,zz}+I_{6,xx}</math> | |<math>I_{7} = m_{3}*l_{3,y}^2+I_{3,xx}-I_{3,yy}+m_{4}*l_{4,z}^2+2*m_{4}*d_{4}*l_{4,z}+(m_{4}+m_{5}+m_{6})*(d_{4}^2-a_{3}^2)+I_{4,yy}-I_{4,yy}+I_{5,zz}-I_{5,yy}+m_{6}*l_{6,z}^2-I_{6,zz}+I_{6,xx}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |8 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{8} = -m_{4}*(d_{2}+d_{3})*(d_{4}+l_{4,z})-(m_{3}+m_{6})*(d_{2}+d_{3})*d_{4}+m_{3}*l_{3,y}*l_{3,z}+m_{3}*(d_{2}+d_{3})*l_{3,y}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |9 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{9} = m_{2}*l_{2,y}*(d_{2}+l_{2,z})</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{10} = 2*m_{4}*a_{5}*l_{4,z}+2*(m_{4}+m_{5}+m_{6})*a_{3}*d_{4}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |11 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{11} = -2*m_{2}*l_{2,x}*l_{2,y}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |12 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{12} = (m_{4}+m_{5}+m_{6})*a_{2}*a_{3}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |13 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{13} = (m_{4}+m_{5}+m_{6})*a_{3}*(d_{2}+d_{3})</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |14 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{14} = I_{4,zz}+I_{5,yy}+I_{6,zz}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |15 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{15} = m_{6}*d_{4}*l_{6,z}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |16 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{16} = m_{6}*a_{2}*l_{6,z}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |17 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{17} = I_{5,zz}+I_{6,xx}+m_{6}*l_{6,z}^2</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |18 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{18} = m_{6}*(d_{2}+d_{3})*l_{6,z}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |19 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{19} = I_{4,yy}-I_{4,xx}+I_{5,zz}-i_{5,yy}+m_{6}*l_{6,z}^2+I_{6,xx}-I_{6,zz}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |20 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{20} = I_{5,yy}-I_{5,xx}-m_{6}*l_{6,z}^2+I_{6,zz}-I_{6,xx}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |21 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{21} = I_{4,xx}-I_{4,yy}+I_{5,xx}-I_{5,zz}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |22 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{22} = m_{6}*a_{3}*l_{6,z}</math> | ||
| + | |kg/m^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |23 | ||
| + | |<math>I_{23} = I_{6,zz}</math> | ||
|kg/m^2 | |kg/m^2 | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:07, 16 October 2017
This page gives an overview over all implemented dynamic models.
General considerations
- Friction is handled on axis basis. The parameters for friction are set for each axis separately.
- Torque (Force) is always expressed in [Nm] ([N])
Contents
Rotational Axes
Dynamic Model 1 - simple rotary axis
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total moment of inertia around the rotation axis of the moved part |
- Model equation
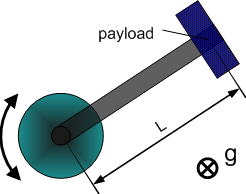
Dynamic Model 2 - horizontal crank-arm axis
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total moment of inertia around the rotation axis of the moved part | |
| 2 | Square of length of crank arm (axis to payload) |
- Model equation
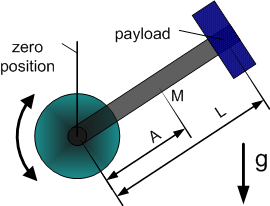
Dynamic Model 3 - vertical crank-arm axis
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total moment of inertia around the rotation axis of the moved part | |
| 2 | Square of length of crank arm (axis to payload) | |
| 3 | Mass (without payload) * Gravity * Distance to center of mass | |
| 4 | Gravity * Distance to Payload |
- Model equation
Linear Axes
Dynamic Model 1 - horizontal axis
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total mass of the moved part. |
- Model equation
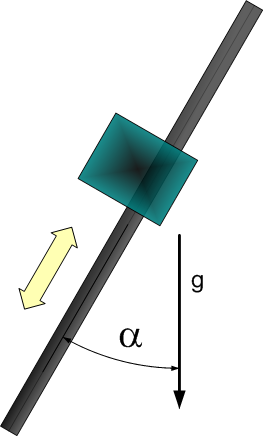
Dynamic Model 2 - vertical or tilted axis
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total mass of the moved part. | |
| 2 | Constant force due to gravity. | |
| 3 | Gravity coefficient used to consider payload mass. (g = 9.80665) |
- Model equation
Traverse Arm Robots
Dynamic Model 1
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 |
Scara Robots
Dynamic Model 1
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 |
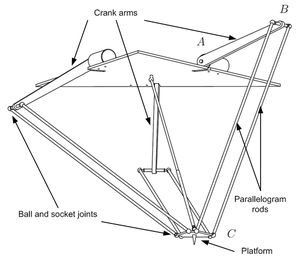
Delta Robots
Dynamic Model 1
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | kg*m2 | |
| 2 | kg*m2/sec2 | |
| 3 | kg | |
| 4 | kg*m2 | |
| 5 | kg | |
| 6 | kg | |
| 7 | kg*m2 | |
| 8 | kg*m2 | |
| 9 | m | |
| 10 | m | |
| 11 | ||
| 12 | ||
| 13 | ||
| 14 |
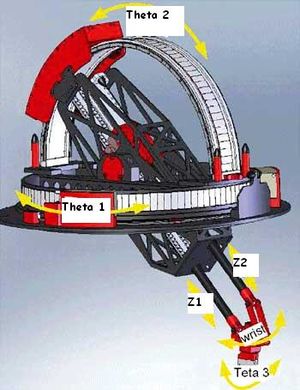
Puma Robots
Dynamic Model 1
Description:
- - Gravity constant
- - Mass of the ith link
- - length of the common normal between the ith and ith+1 joints
- - offset along z axis between the ith and ith+1 joints
- - The distance from the ith joint to the center of mass of the ith link
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | |
kg/m^2 |
| 2 | kg/m^2 | |
| 3 | kg/m^2 | |
| 4 | kg/m^2 | |
| 5 | kg/m^2 | |
| 6 | kg/m^2 | |
| 7 | kg/m^2 | |
| 8 | kg/m^2 | |
| 9 | kg/m^2 | |
| 10 | kg/m^2 | |
| 11 | kg/m^2 | |
| 12 | kg/m^2 | |
| 13 | kg/m^2 | |
| 14 | kg/m^2 | |
| 15 | kg/m^2 | |
| 16 | kg/m^2 | |
| 17 | kg/m^2 | |
| 18 | kg/m^2 | |
| 19 | kg/m^2 | |
| 20 | kg/m^2 | |
| 21 | kg/m^2 | |
| 22 | kg/m^2 | |
| 23 | kg/m^2 |
Dynamic Model 2 - Gravity
Description:
- - The gravity constant
- - The mass of the ith link
- - The length of the ith link
- - The distance from the ith joint to the center of mass of the ith link
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | kg*m^2/s^2 | |
| 2 | kg*m^2/s^2 | |
| 3 | kg*m^2/s^2 | |
| 4 | kg*m^2/s^2 |
Galileo Spherical Robots (GSR)
Dynamic Model 1
| Number | Parameter | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | mP | Payload mass [kg] |
| 2 | mB | Balance mass [kg] |
| 3 | TP | Payload mass center distance from the flange [mm] |
| 4 | TB | Balance mass center distance from the (0,0) [mm] |
| 5 | IR | Inertia of the payload around roll [kg*m2 |