Difference between revisions of "Modbus Communication API"
(Added valid input parameters and error codes) |
(Added valid input parameters and error codes) |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
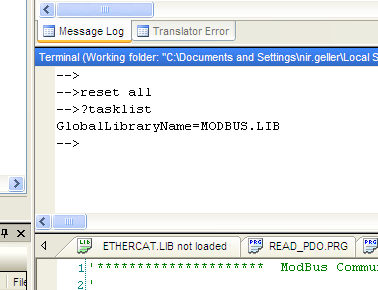
#: The system's response: <pre>GlobalLibraryName=MODBUS.LIB</pre> | #: The system's response: <pre>GlobalLibraryName=MODBUS.LIB</pre> | ||
#:This indicates that library MODBUS.LIB has been loaded globally. | #:This indicates that library MODBUS.LIB has been loaded globally. | ||
| + | #:[[File:softMC_Modbus_HMI_(2).png|400px]] | ||
# That's it! You're now ready to configure the Modbus system. | # That's it! You're now ready to configure the Modbus system. | ||
== Initializing a Modbus Server == | == Initializing a Modbus Server == | ||
| Line 277: | Line 278: | ||
=== Client Components === | === Client Components === | ||
==== Reading ==== | ==== Reading ==== | ||
| + | * The following functions read variables from the different types of registers in a REMOTE modbus server. | ||
| + | * The read value is inserted into an existing variable from the appropriate type (long/double). | ||
| + | * The functions return 0 on success or an error code (not 0) on failure. | ||
===== Reading from Holding registers ===== | ===== Reading from Holding registers ===== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_LONG([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_LONG([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) | ||
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_SHORT( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) |
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_FLOAT( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) |
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_DOUBLE( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) |
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===== Reading from Bits registers ===== | ===== Reading from Bits registers ===== | ||
| Line 289: | Line 293: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_LONG ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_LONG ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) | ||
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_SHORT( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) |
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_FLOAT( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) |
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_DOUBLE( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) |
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===== Reading from Input Bits registers ===== | ===== Reading from Input Bits registers ===== | ||
<pre>val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INBITS ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[num of bits],[dest arr ptr])</pre> | <pre>val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INBITS ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[num of bits],[dest arr ptr])</pre> | ||
| + | ===== Valid Parameters ===== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Parameter | ||
| + | ! Valid Input | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Handle | ||
| + | | The client's unique identifier (received on client creation). | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | DeviceID | ||
| + | | The remote server(slave)'s device ID. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Addr | ||
| + | | The index of the register to read from. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Num of bits (Reading bits) | ||
| + | | The number of bits to read. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | dest ptr / dest arr ptr | ||
| + | | The variable to store the read data. When reading bits, this must be an array of longs in the appropriate size (>= Num of bits). | ||
| + | |} | ||
==== Writing ==== | ==== Writing ==== | ||
| + | * The following functions write data from existing variables to the different types of registers in a REMOTE modbus server. | ||
| + | * The functions return 0 on success or an error code (not 0) on failure. | ||
===== Writing to Holding registers ===== | ===== Writing to Holding registers ===== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_LONG([ | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_LONG([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) |
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_SHORT( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) |
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_FLOAT( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) |
| − | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_DOUBLE( | + | Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) |
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===== Writing to Bits registers ===== | ===== Writing to Bits registers ===== | ||
| − | <pre>val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_BIT([ | + | <pre>val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_BIT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr])</pre> |
| + | ===== Valid Parameters ===== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Parameter | ||
| + | ! Valid Input | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Handle | ||
| + | | The client's unique identifier (received on client creation). | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | DeviceID | ||
| + | | The remote server(slave)'s device ID. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Addr | ||
| + | | The index of the register to start writing to. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | src ptr | ||
| + | | The variable that stores the data to be written. This must be a variable from the appropriate type. | ||
| + | |} | ||
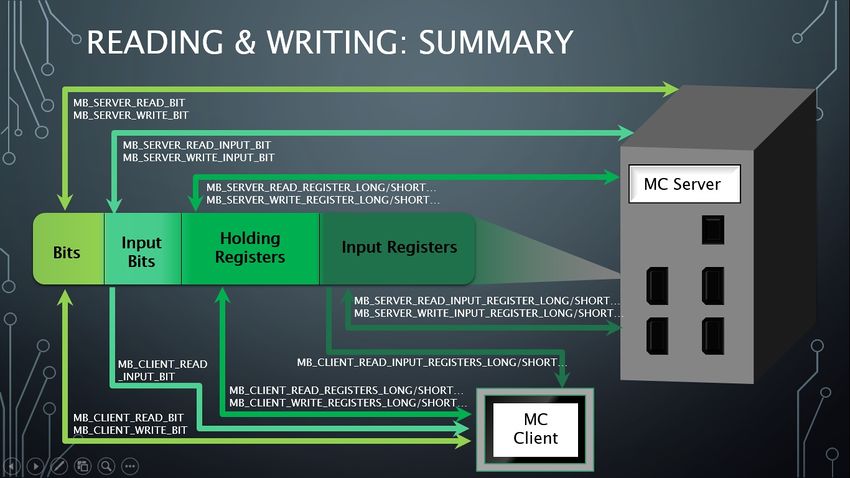
=== Reading and Writing Summary === | === Reading and Writing Summary === | ||
[[File:modbus;newAPI-readwriteSummary.jpg|850px]] | [[File:modbus;newAPI-readwriteSummary.jpg|850px]] | ||
Revision as of 07:38, 17 April 2016
Contents
Overview
Basic Overview
- This describes how to set up Modbus communication for the softMC, and how to generate softMC scripts to handle Modbus communication.
- It is assumed you are familiar with the principles of Modbus communication, although some of them will be described in this page.
- It is also assumed your are familiar with the softMC, ControlStudio and MC-Basic programming.
Modbus Communication Background
- A Motion Controller (MC) can act as a server (slave), a client (master) or both at the same time.
- Each MC connection (TCP/RTU) can be used either as a server component (if the connection is used by the MC’s server-side) or as a client component (if the connection is used by the MC’s client-side).
- Each component has its own parameters that defines it.
- When the MC acts as a server, all server components share the same memory address space, thus acting as one server with multiple connections.
- Each server (slave) on a Modbus network has its own deviceID, which is a number between 1 and 247.
The Modbus server registers
- There are 4 types of registers in the Modbus Server address space:
- Bits (1-bit registers)
- Input Bits (1-bit READ-ONLY registers)
- Holding Registers (16-bit registers)
- Input Registers (16-bit READ-ONLY registers)
- Servers can read and write their own address space.
- Clients can read and write a remote server’s address space.
Getting Started
In order to get started in using the Modbus features:
- Download the required files, according to your system's type:
- Required files for modbus_X86.ZIP.
- Required files for ARM systems.
- Using the ControlStudio File Manager, Upload the following files to your MC:
- mb_x86.O (for X86 Systems) / mb_armA9.O (for ARM Systems)
- Modbus.lib
- Access the file CONFIG.PRG and modify the program by adding the following two lines:
- Program
- Oload mb_x86.O
- Load modbus.lib
- ...
- ...
- End Program
- Upload CONFIG.PRG to the softMC.
- Use the ControlStudio Terminal to enter the following:
- That's it! You're now ready to configure the Modbus system.
Initializing a Modbus Server
To initialize the Modbus server address space, call:
?init_multi_server([bits],[input_bits],[holding registers],[input_registers])
- The function prints "success" and returns 0 on success, or return an error code on failure.
- Notice:
- This is NOT required when softMC does not run a modbus server.
- You can call this method only if no servers are running.
Error codes:
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -1 | Memory allocation failure. |
| -2 | Some servers are still running and using an already mapped address space. |
| -3 | Failed to create a modbus mapping. |
Server Components
Adding server components
- Each time you'll add a component, you will receive a handle, which is the component's identifier (for later use).
- It is best to keep this handles in variables inside your program.
Creating a TCP server component
handle = mb_tcp_server_create([port],[deviceID])
- This opens a TCP connection to the server on port [port] with deviceID [deviceID], and starts the created server immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, or an error code on failure.
Error codes:
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -1 | Server address spaces isn't initialized yet, please call "init_multi_server(...) and try again. |
| -2 | Failed to create main socket. |
| -3 | Failed to connect. |
| -4 | Failed to create server thread. |
Creating an RTU server component
handle = mb_rtu_server_create([type],[port],[baudrate],[data bits],[stop bits],[parity],[deviceID])
- This opens an RTU connection with the given parameters, and starts the created server immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, or an error code on failure.
Error codes:
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -1 | Server address spaces isn't initialized yet, please call "init_multi_server(...) and try again. |
| -2 | Invalid device string. |
| -3 | Invalid parity. |
| -4 | Failed opening RTU. |
| -5 | Failed allocating query buffer memory. |
| -6 | Failed to set RTU mode. |
| -7 | Unable to connect. |
| -8 | Failed to create server thread. |
| -9 | The device is already in use by another system component. |
Stopping Server Components
Stopping a specific server component
You can stop a specific server component by passing its handle to:
result = mb_server_stop([handle])
- Given a handle, this will stop and free the memory of the appropriate server component.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Stopping all server components
You can stop all server components with a single call to:
result = mb_server_stop_all
This function will:
- Stop and free all server components.
- Free the shared address space.
- Return 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Client Components
Adding client components
- Each time you'll add a component, you will receive a handle, which is the component's identifier (for later use).
- It is best to keep this handles in variables inside your program.
Adding a TCP Client component
handle = mb_tcp_client_create([ip],[port])
- This will opens a TCP connection to the client on the given ip and port, and start the client immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, -1 on failure.
Adding an RTU Client component
handle = mb_rtu_client_create([type],[port],[baudrate],[data bits],[stop bits],[parity])
- This will open an RTU connection to the client with the given parameters, and start the client immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, -1 on failure.
Stopping client components
A specific client can be stopped by calling:
result = mb_client_stop([handle])
- Given a handle, this will stop and free the memory of the appropriate client component.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Reset the Modbus System
Sometimes, a user may wish to stop all server and client components at once, and reset the Modbus system (for example, when a user want to initialize a different Modbus system). To do that, call:
result = mb_reset
This function:
- Stops all running servers and clients.
- Frees their memory.
- Frees the shared address space.
- Reset the handle counter.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Reading and Writing
- Servers can read and write their own address space.
- Clients can read and write a remote server’s address space.
- Therefore, Servers and clients use different functions to read/write data from the address space.
Server Components
Reading
- The following functions read variables from the different types of registers and return them.
- When a read error occurs, the functions will write [function name] + "ERROR" + [error code] in the Message Log.
Reading from Holding registers
Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_LONG([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_SHORT([index], [byte_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_FLOAT([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_DOUBLE([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap], [long swap])
Reading from Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_READ_BIT([index])
Reading from Input registers
Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_LONG([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_SHORT([index], [byte_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_FLOAT([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_DOUBLE([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap], [long swap])
Reading from Input Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_READ_INBIT([index])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Index | From 0 to the number of registers available. |
| Byte_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Word_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Long_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
Writing
- The following functions write data into the different types of registers.
- When a write error occurs, the functions will write [function name] + "ERROR" + [error code] in the Message Log.
Writing to holding registers
Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_LONG([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_SHORT([index],[new value],[byte swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_FLOAT([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_DOUBLE([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap], [long swap])
Writing to Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_BIT([index],[new value])
Writing to Input registers
Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_LONG([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_SHORT([index],[new value],[byte swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_FLOAT([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_DOUBLE([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap], [long swap])
Writing to Input Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INBIT([index],[value])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Index | From 0 to the number of registers available. |
| New value | The value to write, must be from the appropriate type. |
| Byte_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Word_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Long_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
Error codes
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -1 | Invalid index. |
| -2 | Local server's address space isn't mapped yet. |
| -3 | Failed to catch the register mutex. |
| -4 | Failed to release the register mutex. |
Client Components
Reading
- The following functions read variables from the different types of registers in a REMOTE modbus server.
- The read value is inserted into an existing variable from the appropriate type (long/double).
- The functions return 0 on success or an error code (not 0) on failure.
Reading from Holding registers
Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_LONG([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr])
Reading from Bits registers
val = MB_CLIENT_READ_BITS ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[num of bits],[dest arr ptr])
Reading from Input registers
Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_LONG ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr])
Reading from Input Bits registers
val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INBITS ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[num of bits],[dest arr ptr])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Handle | The client's unique identifier (received on client creation). |
| DeviceID | The remote server(slave)'s device ID. |
| Addr | The index of the register to read from. |
| Num of bits (Reading bits) | The number of bits to read. |
| dest ptr / dest arr ptr | The variable to store the read data. When reading bits, this must be an array of longs in the appropriate size (>= Num of bits). |
Writing
- The following functions write data from existing variables to the different types of registers in a REMOTE modbus server.
- The functions return 0 on success or an error code (not 0) on failure.
Writing to Holding registers
Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_LONG([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr])
Writing to Bits registers
val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_BIT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Handle | The client's unique identifier (received on client creation). |
| DeviceID | The remote server(slave)'s device ID. |
| Addr | The index of the register to start writing to. |
| src ptr | The variable that stores the data to be written. This must be a variable from the appropriate type. |