Difference between revisions of "Modbus Communication API/zh-hans"
(Created page with "{{Languages}} == Overview == === Basic Overview === * This describes how to set up Modbus communication for the softMC, and how to generate softMC scripts to handle Modbus com...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Languages}} | {{Languages}} | ||
| − | == | + | == 概述 == |
| − | === | + | === 基本概述 === |
| − | * | + | * 本章节介绍如何为softMC设置Modbus通信,以及如何生成softMC脚本来处理Modbus通信。 |
| − | * | + | * 假设您熟悉Modbus通信的原理,尽管其中一些将在此页面中进行描述。 |
| − | * | + | * 假设您熟悉softMC,ControlStudio和MC-Basic编程。 |
| − | === | + | === Modbus通信背景 === |
| − | * | + | * 运动控制器(MC)可以为服务器(从站),客户端(主站)或两者同时充当。 |
| − | * | + | * 每个MC连接(TCP / RTU)可以用作服务器组件(如果连接由MC的服务器端使用)或客户端组件(如果连接由MC的客户端使用)。 |
| − | * | + | * 每个组件都有自己的参数定义。 |
| − | * | + | * 当MC作为服务器时,所有服务器组件共享“相同”的内存地址空间,从而充当具有多个连接的一个服务器。 |
| − | * | + | * Modbus网络上的每个服务器(从站)都有自己的deviceID,它是1到247之间的数字。 |
| − | === | + | === Modbus服务器寄存器 === |
| − | * | + | * Modbus服务器地址空间中有4种寄存器类型: |
| − | *# | + | *# 位(1位寄存器) |
| − | *# | + | *# 输入位(1位READ-ONLY寄存器) |
| − | *# | + | *# 保持寄存器(16位寄存器) |
| − | *# | + | *# 输入寄存器(16位只读寄存器) |
| − | * | + | * 服务器可以读写自己的地址空间 |
| − | * | + | * 客户端可以读写远程服务器的地址空间 |
| − | == | + | == 入门 == |
| − | + | 为了开始使用Modbus功能: | |
| − | # | + | # 下载所需的文件: [[:File:MB_Required_files.zip]] |
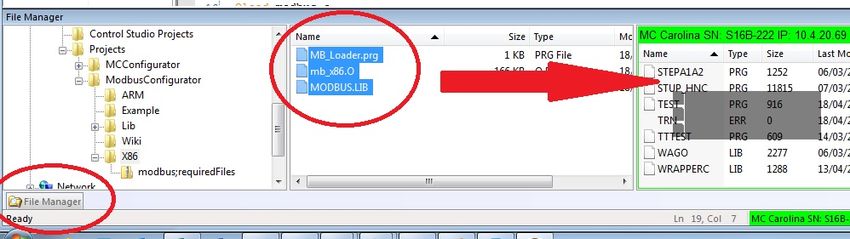
| − | # | + | # 使用ControlStudio文件管理器,将以下文件上传到您的MC: |
#* mb_x86.O ''(for softMC7 )'' / mb_armA9.O ''(for softMC3)'' | #* mb_x86.O ''(for softMC7 )'' / mb_armA9.O ''(for softMC3)'' | ||
#* Modbus.lib | #* Modbus.lib | ||
#* MB_Load.prg | #* MB_Load.prg | ||
#:[[File:modbus;newAPI-upload.jpg|850px]] | #:[[File:modbus;newAPI-upload.jpg|850px]] | ||
| − | # | + | # 通过键入以下命令加载MB_Load.prg: <pre>Load MB_Load.prg</pre> |
| − | #: | + | #:这将加载mb_x86.O / mb_armA9.O,具体取决于您当前的系统,以及Modbus.LIB库文件。 |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''或者''', 您可以通过键入来手动加载对象文件和Modbus库: |
#:<Pre> | #:<Pre> | ||
#::Oload mb_x86.O | #::Oload mb_x86.O | ||
#::Loadglobal Modbus.LIB</pre> | #::Loadglobal Modbus.LIB</pre> | ||
| − | + | 现在可以配置Modbus系统。 | |
| − | == | + | == 初始化Modbus环境 == |
| − | + | 要初始化Modbus环境,包括服务器地址空间,调用: | |
<pre>?init_multi_server([bits],[input_bits],[holding registers],[input_registers])</pre> | <pre>?init_multi_server([bits],[input_bits],[holding registers],[input_registers])</pre> | ||
| − | * | + | * 该功能打印"success",成功返回0,或者失败时返回错误代码。 |
| − | * <u>''' | + | * <u>'''注意:'''</u> 即使您只需要Client组件,您也必须调用此方法。 在这种情况下,只需传递0作为所需的寄存器大小 |
| − | * <u>''' | + | * <u>'''注意:'''</u> 只有在没有活动的服务器组件时,才可以调用此方法。 |
| − | <u>''' | + | <u>'''错误代码:'''</u> |
{| class="wikitable" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! 错误 |
| − | ! | + | ! 含义 |
|- | |- | ||
| -1 | | -1 | ||
Revision as of 03:34, 4 July 2017
| 语言: | [[::Modbus Communication API|English]] • [[::Modbus Communication API/zh-hans|中文(简体)]] |
|---|
Contents
- 1 概述
- 2 入门
- 3 初始化Modbus环境
- 4 Server Components
- 5 Client Components
- 6 Reset the Modbus System
- 7 Reading and Writing
- 8 Modbus Configurator
- 9 HMI IDEs and .CSV Files
概述
基本概述
- 本章节介绍如何为softMC设置Modbus通信,以及如何生成softMC脚本来处理Modbus通信。
- 假设您熟悉Modbus通信的原理,尽管其中一些将在此页面中进行描述。
- 假设您熟悉softMC,ControlStudio和MC-Basic编程。
Modbus通信背景
- 运动控制器(MC)可以为服务器(从站),客户端(主站)或两者同时充当。
- 每个MC连接(TCP / RTU)可以用作服务器组件(如果连接由MC的服务器端使用)或客户端组件(如果连接由MC的客户端使用)。
- 每个组件都有自己的参数定义。
- 当MC作为服务器时,所有服务器组件共享“相同”的内存地址空间,从而充当具有多个连接的一个服务器。
- Modbus网络上的每个服务器(从站)都有自己的deviceID,它是1到247之间的数字。
Modbus服务器寄存器
- Modbus服务器地址空间中有4种寄存器类型:
- 位(1位寄存器)
- 输入位(1位READ-ONLY寄存器)
- 保持寄存器(16位寄存器)
- 输入寄存器(16位只读寄存器)
- 服务器可以读写自己的地址空间
- 客户端可以读写远程服务器的地址空间
入门
为了开始使用Modbus功能:
- 下载所需的文件: File:MB_Required_files.zip
- 使用ControlStudio文件管理器,将以下文件上传到您的MC:
- mb_x86.O (for softMC7 ) / mb_armA9.O (for softMC3)
- Modbus.lib
- MB_Load.prg
- 通过键入以下命令加载MB_Load.prg:
Load MB_Load.prg
- 这将加载mb_x86.O / mb_armA9.O,具体取决于您当前的系统,以及Modbus.LIB库文件。
- 或者, 您可以通过键入来手动加载对象文件和Modbus库:
- Oload mb_x86.O
- Loadglobal Modbus.LIB
现在可以配置Modbus系统。
初始化Modbus环境
要初始化Modbus环境,包括服务器地址空间,调用:
?init_multi_server([bits],[input_bits],[holding registers],[input_registers])
- 该功能打印"success",成功返回0,或者失败时返回错误代码。
- 注意: 即使您只需要Client组件,您也必须调用此方法。 在这种情况下,只需传递0作为所需的寄存器大小
- 注意: 只有在没有活动的服务器组件时,才可以调用此方法。
错误代码:
| 错误 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| -1 | Memory allocation failure. |
| -2 | Some servers are still running and using an already mapped address space. |
| -3 | Failed to create a modbus mapping. |
Server Components
Adding server components
- Each time you'll add a component, you will receive a handle, which is the component's identifier (for later use).
- It is best to keep this handles in variables inside your program.
Creating a TCP server component
handle = mb_tcp_server_create([port],[deviceID])
- This opens a TCP connection to the server on port [port] with deviceID [deviceID], and starts the created server immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, or an error code on failure.
Error codes:
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -1 | Server address spaces isn't initialized yet, please call "init_multi_server(...) and try again. |
| -2 | Failed to create main socket. |
| -3 | Failed to connect. |
| -4 | Failed to create server thread. |
Creating an RTU server component
handle = mb_rtu_server_create([type],[port],[baudrate],[data bits],[stop bits],[parity],[deviceID])
- This opens an RTU connection with the given parameters, and starts the created server immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, or an error code on failure.
Error codes:
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -1 | Server address spaces isn't initialized yet, please call "init_multi_server(...) and try again. |
| -2 | Invalid device string. |
| -3 | Invalid parity. |
| -4 | Failed opening RTU. |
| -5 | Failed allocating query buffer memory. |
| -6 | Failed to set RTU mode. |
| -7 | Unable to connect. |
| -8 | Failed to create server thread. |
| -9 | The device is already in use by another system component. |
Stopping Server Components
Stopping a specific server component
You can stop a specific server component by passing its handle to:
result = mb_server_stop([handle])
- Given a handle, this will stop and free the memory of the appropriate server component.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Stopping all server components
You can stop all server components with a single call to:
result = mb_server_stop_all
This function will:
- Stop and free all server components.
- Free the shared address space.
- Return 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Client Components
Adding client components
- Each time you'll add a component, you will receive a handle, which is the component's identifier (for later use).
- It is best to keep this handles in variables inside your program.
Adding a TCP Client component
handle = mb_tcp_client_create([ip],[port])
- This will opens a TCP connection to the client on the given ip and port, and start the client immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, -1 on failure.
Adding an RTU Client component
handle = mb_rtu_client_create([type],[port],[baudrate],[data bits],[stop bits],[parity])
- This will open an RTU connection to the client with the given parameters, and start the client immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, -1 on failure.
Stopping client components
A specific client can be stopped by calling:
result = mb_client_stop([handle])
- Given a handle, this will stop and free the memory of the appropriate client component.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Reset the Modbus System
Sometimes, a user may wish to stop all server and client components at once, and reset the Modbus system (for example, when a user want to initialize a different Modbus system). To do that, call:
result = mb_reset
This function:
- Stops all running servers and clients.
- Frees their memory.
- Frees the shared address space.
- Reset the handle counter.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Notice: This function is called automatically when calling reset all.
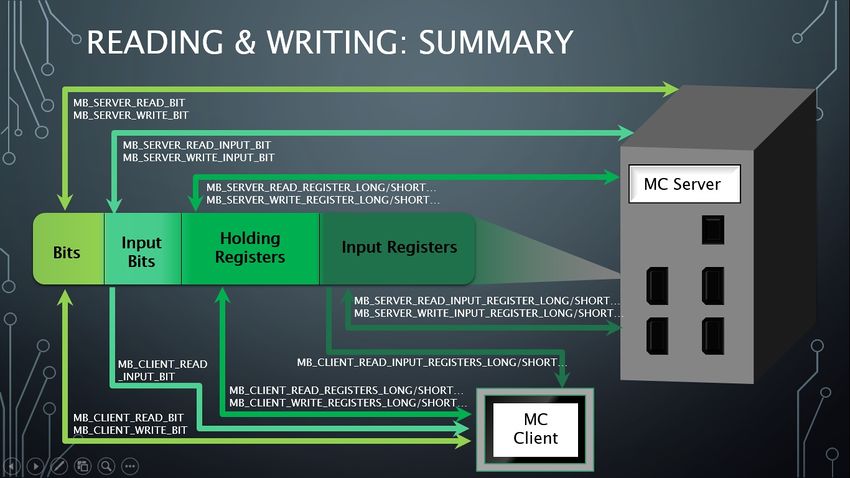
Reading and Writing
- Servers can read and write their own address space.
- Clients can read and write a remote server’s address space.
- Therefore, Servers and clients use different functions to read/write data from the address space.
Server Components
Reading
- The following functions read variables from the different types of registers and return them.
- When a read error occurs, the functions will write [function name] + "ERROR" + [error code] in the Message Log.
Reading from Holding registers
Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_LONG([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_SHORT([index], [byte_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_FLOAT([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_DOUBLE([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap], [long swap])
Reading from Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_READ_BIT([index])
Reading from Input registers
Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_LONG([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_SHORT([index], [byte_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_FLOAT([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_DOUBLE([index], [byte_swap], [word_swap], [long swap])
Reading from Input Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_READ_INBIT([index])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Index | From 0 to the number of registers available. |
| Byte_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Word_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Long_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
Writing
- The following functions write data into the different types of registers.
- When a write error occurs, the functions will write [function name] + "ERROR" + [error code] in the Message Log.
Writing to holding registers
Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_LONG([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_SHORT([index],[new value],[byte swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_FLOAT([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_REG_DOUBLE([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap], [long swap])
Writing to Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_BIT([index],[new value])
Writing to Input registers
Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_LONG([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_SHORT([index],[new value],[byte swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_FLOAT([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap]) Val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INREG_DOUBLE([index],[new value],[byte swap], [word swap], [long swap])
Writing to Input Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_WRITE_INBIT([index],[value])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Index | From 0 to the number of registers available. |
| New value | The value to write, must be from the appropriate type. |
| Byte_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Word_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
| Long_swap | 1 or 0 (True/False) |
Error codes
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -1 | Invalid index. |
| -2 | Local server's address space isn't mapped yet. |
| -3 | Failed to catch the register mutex. |
| -4 | Failed to release the register mutex. |
Client Components
Reading
- The following functions read variables from the different types of registers in a REMOTE modbus server.
- The read value is inserted into an existing variable from the appropriate type (long/double).
- The functions return 0 on success or an error code (not 0) on failure.
Reading from Holding registers
Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_LONG([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_REG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr])
Reading from Bits registers
val = MB_CLIENT_READ_BITS ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[num of bits],[dest arr ptr])
Reading from Input registers
Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_LONG ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INREG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[dest ptr])
Reading from Input Bits registers
val = MB_CLIENT_READ_INBITS ([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[num of bits],[dest arr ptr])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Handle | The client's unique identifier (received on client creation). |
| DeviceID | The remote server(slave)'s device ID. |
| Addr | The index of the register to read from. |
| Num of bits (Reading bits) | The number of bits to read. |
| dest ptr / dest arr ptr | The variable to store the read data. When reading bits, this must be an array of longs in the appropriate size (>= Num of bits). |
Writing
- The following functions write data from existing variables to the different types of registers in a REMOTE modbus server.
- The functions return 0 on success or an error code (not 0) on failure.
Writing to Holding registers
Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_LONG([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_SHORT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_FLOAT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr]) Val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_REG_DOUBLE([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr])
Writing to Bits registers
val = MB_CLIENT_WRITE_BIT([handle],[deviceID],[addr],[src ptr])
Valid Parameters
| Parameter | Valid Input |
|---|---|
| Handle | The client's unique identifier (received on client creation). |
| DeviceID | The remote server(slave)'s device ID. |
| Addr | The index of the register to start writing to. |
| src ptr | The variable that stores the data to be written. This must be a variable from the appropriate type. |
Reading and Writing Summary
Modbus Configurator
Background
General
The Modbus Communication Scripts Generator (Modbus Configurator) is a tool that allows you to map your softMC application variables to Modbus tags.
Note: Tag access is defined from the HMI perspective. In other words:
- Read Access variables are written by the softMC to the Modbus address space.
- Write Access variables are read by the softMC from the Modbus address space.
You can define whether a variable has Read Access, or Write Access. Currently, it is not possible to define a variable as having both Read Access and Write Access. However, all Write Access variables can be written once by the softMC upon system startup by a special routine that is generated in HMIMBMAP.LIB (see section below).
The MCMBConfigurator creates three files:
- HMIMBMAP.LIB and HMIMBMAP.PRG files are MC-Basic scripts that are used to start a softMC task. These are default file names, which you can change, but must retain the 8.3 format. This task cyclically and indefinitely reads/writes Modbus tags according to access type.
- A .CSV format file that can be used by an HMI development environment, such as JMobile Studio or Indusoft, to automatically import Modbus tags. You define the HMI development environment by selecting various Python scripts that will generate the .csv file.
Mapping Variables
- Variables destined to be mapped to Modbus tags must be defined as global variables by the common Shared declaration.
- In order to map the variables, the program must be loaded in the softMC.
Getting Started
- Start the Modbus Configurator: from the ControlStudio toolbar, select Tools > Modbus Configurator. The Modbus Configurator tool will appear.
- From the top menu, Select Connection > Setting.
- Enter the MC's IP and port (default connection port is 5001), then click OK.
- From the top menu, Select Connection > Connect.
- Configure the Modbus Address Space
- From the top menu, Select Modbus Comm. Settings.
- In the General tab, Select the appropriate python script.
- In the Registers tab, enter the amount of registers needed per type, and the registers offset (Optional).
- Notice: The maximum register number is 65536.
- In the Connections tab, add the server connections (TCP/RTU).
- Click OK.
- Map your variables
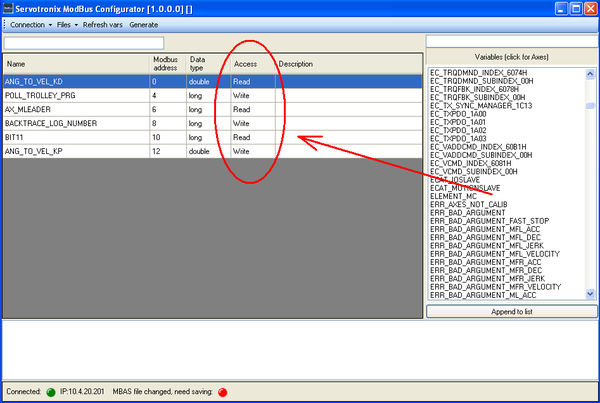
- Once the Modbus Configurator is connected to softMC it gets updated with the complete list of all the global variables. Double-clicking on variables automatically maps them to Modbus tags in consecutive order. The automatic Modbus address and data type are displayed in the table, along with the Modbus address space area in which the data will be stored (Default: Holding Registers).
- If a mapped variable is defined as CONST, its access type will automatically set to "Read". In such instances the access type cannot be changed. "Read Access variables are read only by the HMI; therefore the softMC only writes them to the Modbus address space.
- If a mapped variable is not defined as CONST, it automatically appears with "Write" Access. Double-click on the access type to toggle the variable between Read Access and Write Access, and thus determine whether the variable will be read or written by softMC.
Generating and Using Scripts
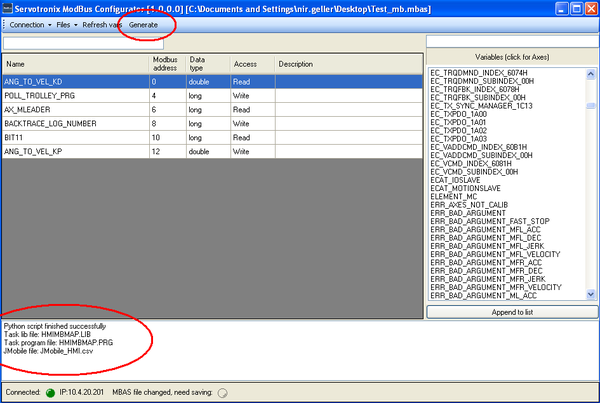
After you are done mapping variables and defining the access types, a snapshot of the current configuration must be saved in order to generate the Modbus-handling scripts.
1. Click Files, and then Save As.
- The mapping is saved in an .mbas file.
- If you makes changes after saving the .mbas file, the MBAS file indicator in the status bar will light up.
2. To generate the product files, click Generate.
- The Log windows will display Success messages.
- The product files were created in the target folder you chose when saving the .mbas file.
- The files HMIMBMAP.LIB and HMIMBMAP.PRG will automatically open in ControlStudio.
Using the Modbus-Handling Scripts
1. Using the ControlStudio File Manager, copy HMIMBMAP.LIB and HMIMBMAP.PRG to the softMC.
Note: Before these files can be loaded and used, your application must be loaded, and all mapped variables must exist in the softMC memory.
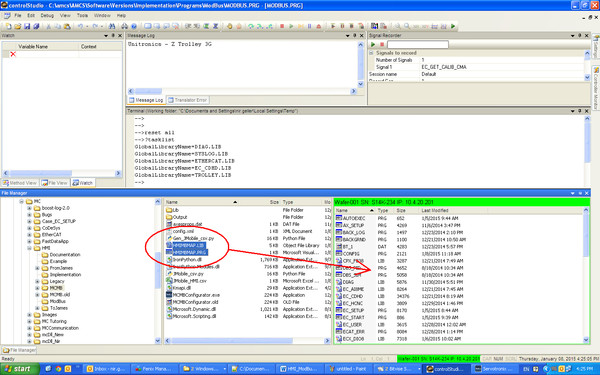
1. Using the ControlStudio Terminal, load the library HMIMBMAP.LIB:
Load HMIMBMAP.LIB
- Since HMIMBMAP.PRG imports this library it must not be loaded globally. This code can be executed wherever is convenient.
2. Verify that the library was loaded successfully:
?tasklist
3. Start the Modbus communication task by loading the program:
Load HMIMBMAP.PRG
HMIMBMAP.PRG is defined as Program Continue, therefore it starts automatically after it is loaded and it does not require an explicit StartTask command.
Of course, HMIMBMAP.PRG can be loaded and executed only after HMIMBMAP.LIB is loaded. Therefore, you should add the following code to AUTOEXEC.PRG or wherever is convenient:
Load HMIMBMAP.LIB Load HMIMBMAP.PRG
HMIMBMAP.PRG Explained
The code:
import HMIMBMAP.LIB Program Continue dim retVal as long = 0 retVal = Init_Modbus while 1 retVal = Read_Modbus_Registers retVal = Write_Modbus_Registers sleep 1 end while End Program
The functions Init_Modbus, Read_Modbus_Registers and Write_Modbus_Registers are implemented in HMIMBMAP.LIB, which is automatically generated by a Python script.
The function Init_Modbus starts the Modbus server and then writes to the Modbus address space all the Write Access Variables (i.e., all the variables read by the softMC from the Modbus address space). This feature allows you to setup the system to start with an initialized Modbus address space before the HMI/PLC connects to it. The HMI/PLC can read the address space and initialize itself accordingly.
The functions Read_Modbus_Registers and Write_Modbus_Registers are invoked cyclically and indefinitely. Read_Modbus_Registers reads all the tags that are written by the HMI/PLC and updates the Write Access variables with new values, while Write_Modbus_Registers does the opposite.
HMI IDEs and .CSV Files
Each line in the .csv file generated by the MCMBConfigurator file holds data about a single variable, such as Modbus address or data type.
This data can be used by an HMI IDE to import Modbus tags and associate them with HMI functionality.
Different manufacturer IDEs use different .csv formatting; therefore, various Python scripts are used to create the specific .csv files suitable for a particular manufacturer IDE.
JMobile Studio
Python script: JMobile_csv.py
Default target .csv file name: JMobile_HMI.csv (user-definable)
To import tags, perform the following procedure in JMobile Studio.
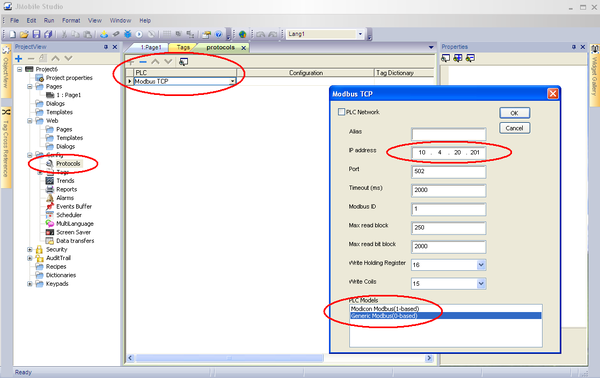
Define Protocol
1. In the ProjectView pane, select Protocols.
2. Click the blue + sign.
3. From the list, select Modbus TCP.
4. In the Modbus TCP configuration window, define:
- IP Address: Set the IP address of your softMC.
- PLC Models: Select Generic Modbus (0-based), meaning the softMC Modbus server starts addressing tags from 0.
- Click OK.
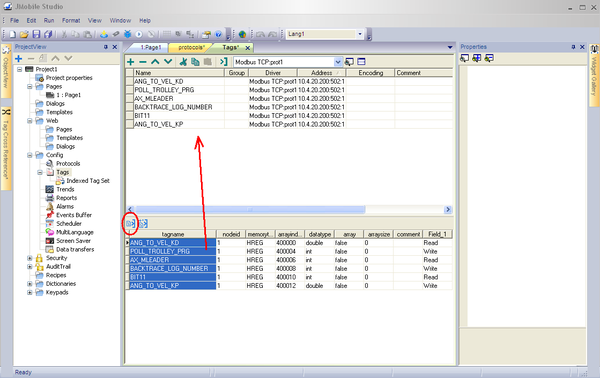
Import Tags
1. In the ProjectView pane, select Tags.
2. From the list, select Modbus TCP protocol defined previously.
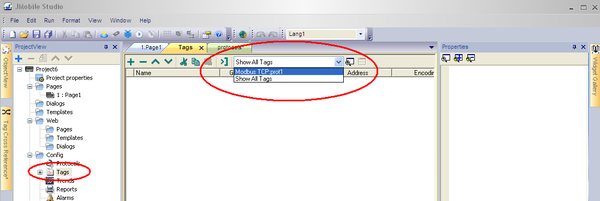
3. Click the Import Tags button.
4. Open the generated file JMobile_HMI.csv.
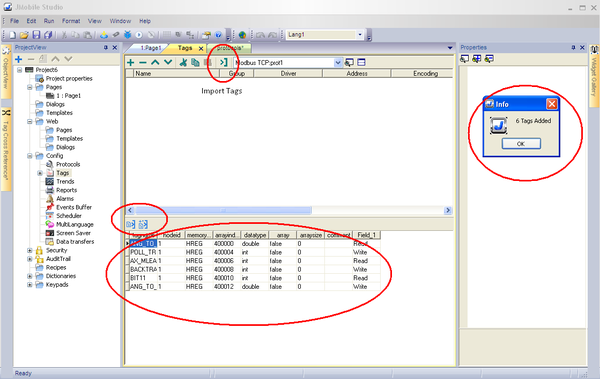
5. Select the tags you want to add to your project, and click the Import tags button.
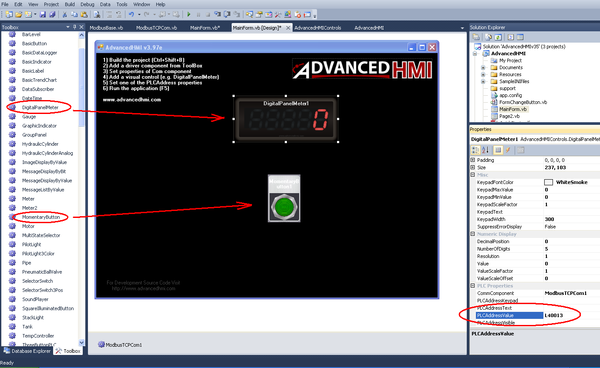
AdvancedHMI
AdvancedHMI is an open source project (http://www.advancedhmi.com/), which is downloaded as a Visual Basic project. You can then open the project, add widgets, compile, and run it.
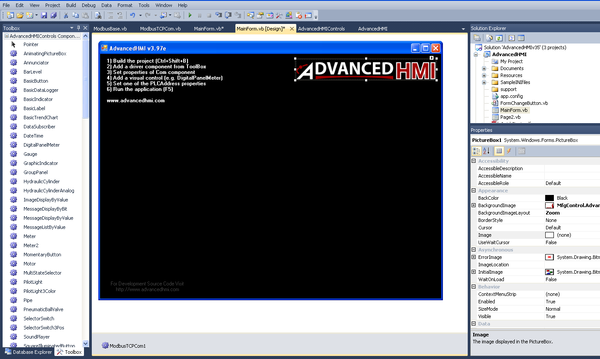
1. Drag and drop ModbusTCPCom into MainForm.vb [Design].
2. The driver appears the bottom of the screen (circled in green).
- Click the driver, and then use the Properties pane (circled in red) to setup the IP address of the Modbus server.
- For example, drag and drop DigitalPanelMeter and MomentaryButton into MainForm.vb [Design].
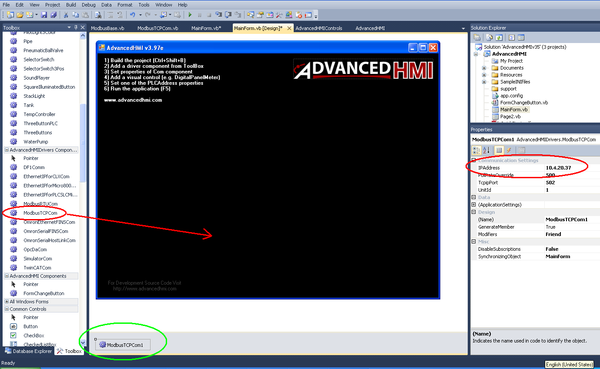
3. For both widgets, use the Properties pane to set the Modbus address that is associated with the variables from the softMC application.
- MC Modbus server addressing starts from 40000.
- AdvancedHMI Modbus client addressing starts from 40001.
- Prefix the address with the letter L.
4. Save the project (Ctrl+S).
5. Build the project (Ctrl+Shift+B).
6. Run the project (F5).