Difference between revisions of "Teach Pendant Operation Guide"
m (→Program Screen) |
(BackToTop button) |
||
| (77 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Languages|Teach_Pendant_Operation_Guide}} | ||
| + | <div id="BackToTop" class="noprint" style="background-color:; position:fixed; bottom:32px; left:95%; z-index:9999; padding:0; margin:0;"> | ||
| + | <span style="color:blue; font-size:8pt; font-face:verdana,sans-serif; border:0.2em outset:#ceebf7; padding:0.1em; font-weight:bolder; -moz-border-radius:8px; "> | ||
| + | [[Image:TOP2.png|50px|link=#top]] </span></div> | ||
= Overview = | = Overview = | ||
| − | The softTP is a teach pendant (TP) designed for use with softMC 3 and softMC 7 motion controllers and various types of robots, | + | The softTP is a teach pendant (TP) designed for use with softMC 3 and softMC 7 motion controllers and various types of robots, such as SCARA, PUMA and DELTA. The softTP allows operators to move the robot by means of jog keys, and to create and run complete robot programs written in MC-Basic. |
| − | such as SCARA, PUMA and | ||
The softTP touch screen interface enables quick and easy application development. The softTP software package also includes a | The softTP touch screen interface enables quick and easy application development. The softTP software package also includes a | ||
| Line 8: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:softTP_elements.png|softTP_elements.png]] | [[Image:softTP_elements.png|softTP_elements.png]] | ||
| + | |||
= Access Permission Levels = | = Access Permission Levels = | ||
| Line 15: | Line 19: | ||
* Operator | * Operator | ||
* Programmer | * Programmer | ||
| − | * Administrator | + | * Administrator |
| − | Each softTP user must login with a password for a specific permission level. | + | Each softTP user must login with a password for a specific permission level. |
The following table indicates the functions available to each user level. | The following table indicates the functions available to each user level. | ||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| + | |||
| + | !width="280" bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
| + | !colspan="4" bgcolor= A9A9A9|Permission Level | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
!width="280"| | !width="280"| | ||
| Line 27: | Line 36: | ||
!width="80"|Operator | !width="80"|Operator | ||
!width="80"|Programmer | !width="80"|Programmer | ||
| + | !width="80" bgcolor= A9A9A9|Admin | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 39: | Line 49: | ||
| | | | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 65: | ||
| | | | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 81: | ||
| | | | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Start/stop certain processes (e.g., move?). | |
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | <center></center> | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 77: | Line 99: | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| − | | | + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| |
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Start/stop certain programs. | |
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | <center></center> | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 90: | Line 115: | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| − | | | + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| |
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | View data (variables) but not modify. | |
| | | | ||
| Line 104: | Line 129: | ||
| | | | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | View programs, but not modify. | |
| | | | ||
| Line 117: | Line 145: | ||
| | | | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Acknowledge errors. | |
| | | | ||
| Line 132: | Line 163: | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Enable the robot. | |
| | | | ||
| Line 143: | Line 176: | ||
| | | | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Create and edit user programs (UPG/ULB). | |
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | <center></center> | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 155: | Line 194: | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| − | | | + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| |
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Create and edit (teach) program variables. | |
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | <center></center> | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 167: | Line 209: | ||
| | | | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor= A9A9A9| | ||
| + | <center>x</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |-bgcolor= A9A9A9 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Create and edit all types of MC Basic program files (PRG/LIB & UPG/ULB). | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | <center></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | <center></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | <center></center> | ||
| | | | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| − | |- | + | |-bgcolor= A9A9A9 |
| + | | | ||
| + | Change passwords of all user levels. | ||
| + | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | <center></center> | |
| | | | ||
| Line 184: | Line 245: | ||
<center>x</center> | <center>x</center> | ||
| − | |- | + | |-bgcolor= A9A9A9 |
| + | | | ||
| + | Access the Terminal screen. | ||
| + | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | <center></center> | |
| | | | ||
| Line 198: | Line 262: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This document presents screens as seen by '''PROGRAMMER'''. | ||
=softTP Switches = | =softTP Switches = | ||
| Line 206: | Line 273: | ||
The switch has three positions: released, partially pressed, and fully pressed. | The switch has three positions: released, partially pressed, and fully pressed. | ||
| − | + | In Manual mode, motion and jogging commands can be issued from the teach pendant only when the deadman switch is in the intermediate, partially-pressed position. | |
| − | If the deadman switch is released, or fully pressed, while axes are in motion, the motion stops | + | If the deadman switch is released, or fully pressed, while axes are in motion, the motion stops automatically. |
| − | |||
| + | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| + | |||
| + | !width="60"|Position | ||
| + | !width="100"|State | ||
| + | !width="380"|Description | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |[[File:deadman_1.jpg]] |
| − | '''Deadman | + | | |
| + | '''Deadman Off''' | ||
| | | | ||
* Deadman switch is not pressed or is pressed too lightly. | * Deadman switch is not pressed or is pressed too lightly. | ||
| Line 222: | Line 295: | ||
* softTP cannot issue motion commands. | * softTP cannot issue motion commands. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:deadman_2.jpg]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | '''Deadman | + | '''Deadman On''' |
| | | | ||
* Deadman switch is pressed with normal pressure. | * Deadman switch is pressed with normal pressure. | ||
| Line 230: | Line 304: | ||
* softTP can issue motion commands. | * softTP can issue motion commands. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:deadman_3.jpg]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | '''Deadman | + | '''Deadman Off''' |
| | | | ||
* If deadman switch is pressed too hard. | * If deadman switch is pressed too hard. | ||
| Line 240: | Line 315: | ||
| + | ==Using Emulator== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Set in your browser the following address: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | http:<ip address>/tp/emulator | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where <ip address> is the IP address of your softMC<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | for example: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | http://10.4.20.148:1207/tp/emulator | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
When using TP Emulator, the deadman switch status is represented by the on‑off vertical switch on the left side of the screen. | When using TP Emulator, the deadman switch status is represented by the on‑off vertical switch on the left side of the screen. | ||
| Line 247: | Line 335: | ||
==Emergency Stop == | ==Emergency Stop == | ||
| − | + | Pressing the Emergency switch automatically powers off the motors, stops motion and and disables the axes. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Pressing the Emergency switch automatically powers off the | + | If the robot is equipped with brakes, the brakes are activated. |
| − | motors, stops motion and and disables the axes. | ||
==Mode Selector Switch == | ==Mode Selector Switch == | ||
| Line 256: | Line 343: | ||
The Mode Selector switch on the front of softTP has three positions: Manual, Automatic and External. | The Mode Selector switch on the front of softTP has three positions: Manual, Automatic and External. | ||
| − | If the mode setting is switched from Automatic to Manual | + | If the mode setting is switched from Automatic to Manual while a program is running, program execution stops immediately. |
| + | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| + | |||
| + | !width="100" bgcolor= A9A9A9|Mode | ||
| + | !width="400" bgcolor= A9A9A9|Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
'''Manual''' | '''Manual''' | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Left position. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Manual mode is used for jogging the axes. | |
| + | |||
| + | When in Manual mode, the robot velocity is reduced and the user cannot issue run commands or edit programs. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
'''Automatic''' | '''Automatic''' | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Middle position. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Automatic mode is used for editing/running programs. | |
| + | |||
| + | When in Automatic mode, the axes cannot be jogged. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
'''External''' | '''External''' | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Right position. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | When in External mode, the softTP does not control the robot. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 295: | Line 386: | ||
== Toolbar == | == Toolbar == | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | + | [[Image:softTP toolbar 4.1.jpg]] |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | |
| − | |- | + | |
| − | | | + | !width="60" bgcolor = A9A9A9| |
| + | !width="100" bgcolor = A9A9A9|Toolbar | ||
| + | !width="340" bgcolor = A9A9A9|Description | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
[[Image:1.png|1.png]] | [[Image:1.png|1.png]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Logout | + | '''Logout''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Exits the TP | + | Exits the TP Emulator. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
[[Image:2.png|2.png]] | [[Image:2.png|2.png]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | TP Operation Mode | + | '''TP Operation Mode''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Indicates the teach pendant’s current operation control mode, as defined by the mode selector switch | + | Indicates the teach pendant’s current operation control mode, as defined by the mode selector switch. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | '''Text box''' | |
| | | | ||
| − | Message field for system notifications | + | Message field for system notifications. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
[[Image:4.png|4.png]] | [[Image:4.png|4.png]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Axes in Motion | + | '''Axes in Motion''' |
| | | | ||
Indicates state of the axes:<br> | Indicates state of the axes:<br> | ||
| Line 335: | Line 431: | ||
[[Image:5.png|5.png]] | [[Image:5.png|5.png]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Primary TP | + | '''Primary TP''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Indicates that the teach pendant in use is the primary TP | + | Indicates that the teach pendant in use is the primary TP, if other TPs are connected. |
| + | (Not currently implemented) | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
[[Image:6.png|6.png]] | [[Image:6.png|6.png]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Collapse/Expand | + | '''Collapse/Expand''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Hides/shows the menu bar, to provide additional screen space. | + | Hides/shows the menu bar, to provide additional screen space for program lines. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
[[Image:7.png|7.png]] | [[Image:7.png|7.png]] | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Enable | Disable | + | '''Enable | Disable''' |
| | | | ||
Enables and disables all axes, and indicates the state of the axes.<br> | Enables and disables all axes, and indicates the state of the axes.<br> | ||
| Line 359: | Line 457: | ||
==Menu Bar == | ==Menu Bar == | ||
| − | The menu bar provides access to the softTP screens. | + | The menu bar provides access to the eight softTP screens. |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:menuBar 4.2.jpg|menuBar 4.2.jpg |500px]] |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | + | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" |
| + | |||
| + | !width="80" bgcolor= A9A9A9|'''Screen''' | ||
| + | !width="420" bgcolor= A9A9A9 align="left"|'''Function''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | '''Jog''' | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | Used to select the type of robot, and jog the robot/axes in the user-defined frame.<br> | |
| + | Displays current robot position in Cartesian and joint coordinates. Used to '''teach/set''' new points, and '''move(s)''' to a predefined point.<br> | ||
| + | Provides '''tool-calibration''', and '''align''' functionality. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Program | + | '''Program''' |
| | | | ||
Used to create, edit, run and debug MC‑Basic programs. | Used to create, edit, run and debug MC‑Basic programs. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Data | + | '''Data''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Used to | + | Used to create, edit, run and debug MC-Basic programs. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | IO | + | '''IO''' |
| | | | ||
Used to monitor and switch system digital inputs and outputs. | Used to monitor and switch system digital inputs and outputs. | ||
| − | |- | + | |-bgcolor=D9D9D9 |
| | | | ||
| − | Diagnostics | + | '''Terminal''' |
| + | | | ||
| + | Allows command line entry of MC Basic commands. | ||
| + | Accessible to Administrator-users only. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Diagnostics''' | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Displays | + | Displays settings and status of configured axes and devices. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Errors | + | '''Errors''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Displays the log of faults in the softMC motion controller | + | Displays the log of faults in the softMC motion controller. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Settings | + | '''Settings''' |
| | | | ||
Displays system software components and versions. | Displays system software components and versions. | ||
| + | |-bgcolor=D9D9D9 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''settings''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Allows setting of stystem variables. | ||
| + | Accessible to Administrator-users only. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 413: | Line 521: | ||
==Jog Keys == | ==Jog Keys == | ||
| − | When Frame is set to Joint, keys are labeled according to axes: J1, J2, J3, and so on. | + | [[Image:jog_keys_4.3.1.jpg]] [[Image:jog_keys_4.3.2.jpg]] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | When '''Frame''' is set to Joint, keys are labeled according to axes: J1, J2, J3, and so on. | ||
| − | When Frame is set to Base, Tool or World, keys are labeled according to Cartesian coordinates: X, X, Z, Yaw, Pitch, Roll. | + | When '''Frame''' is set to Base, Tool or World, keys are labeled according to Cartesian coordinates: X, X, Z, Yaw, Pitch, Roll. |
=Domains = | =Domains = | ||
| Line 422: | Line 533: | ||
code. | code. | ||
| − | Every program is associated with a domain. In MC-Basic, domains are implemented by a namespace feature of the MC-Basic language. (Refer | + | Every program is associated with a domain. In MC-Basic, domains are implemented by a '''namespace feature of the MC-Basic language'''. (Refer |
to: http://softmc.servotronix.com/wiki/Namespace). | to: http://softmc.servotronix.com/wiki/Namespace). | ||
All variables of a given domain are automatically saved to a separate file on the softMC disk after they are created or updated. | All variables of a given domain are automatically saved to a separate file on the softMC disk after they are created or updated. | ||
| − | The softTP provides three system domains for certain data, which do not have associated program files | + | The softTP provides three system domains for certain data, which do not have associated program files. |
| + | |||
| + | Every project has automatically associated domain of the same name. | ||
| − | |||
== TP Domain == | == TP Domain == | ||
| − | TP variables are not assigned to a particular project | + | '''TP''' variables are not assigned to a particular program or project. |
They can be used freely as auxiliary variables for debugging and other functions. | They can be used freely as auxiliary variables for debugging and other functions. | ||
| Line 441: | Line 553: | ||
==Base Domain == | ==Base Domain == | ||
| − | Base variables are not assigned to any program and are used to store the base property values used by the selected robot. | + | '''Base''' variables are not assigned to any program and are used to store the '''base''' property values used by the selected robot. |
It is recommended that variables in this domain use the naming format BASE1, BASE2, and so on. | It is recommended that variables in this domain use the naming format BASE1, BASE2, and so on. | ||
| Line 448: | Line 560: | ||
==Tool Domain == | ==Tool Domain == | ||
| − | Tool variables are not assigned to any program and are used to store the tool property values used by the selected robot. | + | '''Tool''' variables are not assigned to any program and are used to store the '''tool''' property values used by the selected robot. |
It is recommended that variables in this domain use the naming format TOOL1, TOOL2, and so on. | It is recommended that variables in this domain use the naming format TOOL1, TOOL2, and so on. | ||
| Line 498: | Line 610: | ||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | !width="80" |Setting |
| − | + | !width="200" |Description | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 512: | Line 623: | ||
Frame | Frame | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Cartesian (Tool, Base and World): Linear movement along X, Y and Z directions, angular motion around a | + | Cartesian (Tool, Base and World): Linear movement along X, Y and Z directions, angular motion around a static XYZ coordinate. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 591: | Line 702: | ||
The file extensions *.UPG user programs and *.ULB for user libraries are used to distinguish user programs from general system programs and settings. | The file extensions *.UPG user programs and *.ULB for user libraries are used to distinguish user programs from general system programs and settings. | ||
| − | + | Administrator level users can access and manipulate both global (*.PRG/*.LIB) and user (*.UPG/*.ULB) programs and libraries. | |
| − | + | Programmer level users can create/edit/run/debug user programs only (*.UPG) and user libraries only (*.ULB). | |
| − | + | '''Projects''' created by programmer level users generate four files: | |
| + | |||
| + | {| | ||
| + | !width= "100"|'''''name''.UPG''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | The main user task. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !width= "100"|'''''name''.ULB''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | The library containing the functions and subroutines used in the main user task. | ||
| + | |- bgcolor = D9D9D9 | ||
| + | !width= "100"|'''''name''.DEF''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | The declarations of all domain variables. (not visible by the user) | ||
| + | |- bgcolor = D9D9D9 | ||
| + | !width= "100"|'''''name''.VAR''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | The currently defined values of the domain variables. (not visible by the user) | ||
| − | + | |} | |
| − | |||
| − | A project | + | A project is set of files with same names but different extension (e.g. TASK.UPG, TASK.ULB, TASK.DEF and TASK.VAR.) Non-Admin users only see files with the extensions UPG and ULB. |
| − | + | [[Image: program screen 7.1.jpg|program screen 7.1.jpg|500px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| + | !width="110" bgcolor = A9A9A9|'''Setting''' | ||
| + | !width="300" bgcolor = A9A9A9|'''Description''' | ||
| − | '''Project Mode''' | + | |- bgcolor= E9E9E9 |
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Project (File) Mode''' | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | PROGRAMMER | |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
'''Open Project''' | '''Open Project''' | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
Opens an existing project. | Opens an existing project. | ||
| Line 628: | Line 753: | ||
| | | | ||
'''New Project''' | '''New Project''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Opens a new project.<br> | ||
| + | When prompted for a name, enter up to 8 characters.<br> | ||
| + | When a new project is created, a user program and user library of the same name are also created. | ||
| + | |- bgcolor = E9E9E9 | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | '''File Mode''' | |
| + | | | ||
| + | ADMINISTRATOR | ||
| − | + | |- bgcolor = E9E9E9 | |
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Open File''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Opens an existing file. | ||
| − | + | |- bgcolor = E9E9E9 | |
| + | | | ||
| + | '''New File''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Open a new file. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 662: | Line 802: | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Stops the program at the end of the line currently being executed | + | Stops the program at the end of the line currently being executed. |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 669: | Line 809: | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Starts execution | + | Starts execution of the program. |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | '''Jump | + | '''Jump to Line''' |
| | | | ||
| Line 699: | Line 839: | ||
Exit the subroutine. | Exit the subroutine. | ||
| − | | | + | |- bgcolor= E9E9E9 |
| − | + | | | |
| − | |||
'''Edit Mode''' | '''Edit Mode''' | ||
| − | + | | | |
Provides the code syntax for commonly used instructions, including prompts for the data required for completing the code line/s. | Provides the code syntax for commonly used instructions, including prompts for the data required for completing the code line/s. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
'''Program''' | '''Program''' | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | Instructions for defining subroutines and functions. | + | Instructions for defining subroutines and functions. <br> |
* Sub ... End Sub | * Sub ... End Sub | ||
* Function | * Function | ||
| Line 723: | Line 857: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | '''Flow | + | '''Flow Commands''' |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | Instructions used to change the flow of a program based on specific conditions. | + | Instructions used to change the flow of a program based on specific conditions.<br> |
* If ... Then ... Else ... End If | * If ... Then ... Else ... End If | ||
* While ... End While | * While ... End While | ||
| Line 736: | Line 869: | ||
| | | | ||
'''Interpolation''' | '''Interpolation''' | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* Move | * Move | ||
* MoveS | * MoveS | ||
| − | * Circle (P2P) | + | * Circle (P2P) |
* Circle (Angle) | * Circle (Angle) | ||
* DoPass | * DoPass | ||
| Line 746: | Line 878: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | '''Motion | + | '''Motion Commands''' |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* Stop | * Stop | ||
| Line 757: | Line 888: | ||
| | | | ||
'''I/O''' | '''I/O''' | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* Inputs | * Inputs | ||
* Outputs | * Outputs | ||
| − | | | + | |- bgcolor = E9E9E9 |
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Project Manager''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | PROGRAMMER | ||
| + | |- bgcolor = E9E9E9 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''File Manager''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | ADMINISTRATOR | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | [Project/File list] | |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
'''Delete''' | '''Delete''' | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
Deletes selected project. | Deletes selected project. | ||
| Line 787: | Line 918: | ||
| | | | ||
'''Save As''' | '''Save As''' | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | saves a copy of current project using a new name. | |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
'''Rename''' | '''Rename''' | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | Rename the current project. | |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 802: | Line 931: | ||
= Data Screen = | = Data Screen = | ||
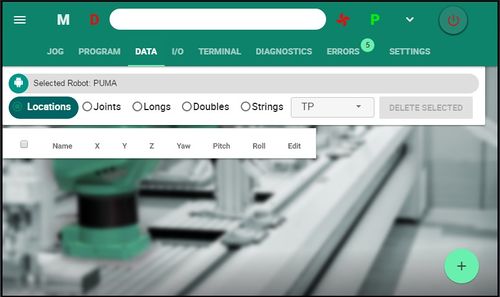
| − | The Data screen is used for creating and editing variables in the domain that is currently selected. | + | The Data screen is used for creating and editing '''variables''' in the domain that is currently selected. |
| − | Variables can be robot positions or any other data | + | Variables can be robot positions or any other data type that is supported in MC‑Basic, such as long, double and string. |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:data screen 8.1.jpg|data screen 8.1.jpg |500px]] |
Select the domain, and the type of variable, then click the + button to create a variable. | Select the domain, and the type of variable, then click the + button to create a variable. | ||
| Line 815: | Line 944: | ||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| − | |- | + | |- bgcolor = A9A9A9 |
| | | | ||
'''Setting''' | '''Setting''' | ||
| Line 822: | Line 951: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
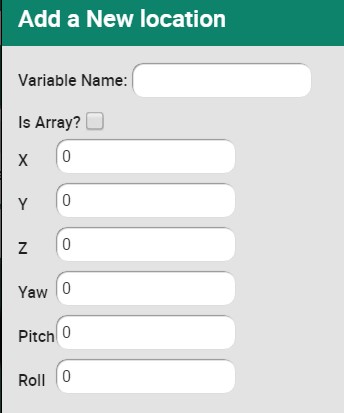
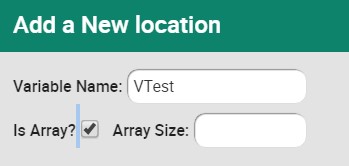
| − | Locations | + | '''Locations''' |
| | | | ||
| − | World/Cartesian positions. | + | World/Cartesian positions. <br> |
| + | [[Image:data_addnewlocation_1.jpg]] [[Image:data_addnewlocation_2.jpg]] <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:data_addnewlocation_3.jpg]]<br> | ||
| + | Checkbox - to select (for deletion) | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Joints | + | '''Joints''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Joint positions. | + | Joint positions.<br> |
| + | [[Image:data_joints.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Longs | + | '''Longs''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Numeric variable: 32-bit integer. | + | Numeric variable: 32-bit integer.<br> |
| + | [[Image:data_longs.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Doubles | + | '''Doubles''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Numeric variable: 64-bit floating point. | + | Numeric variable: 64-bit floating point.<br> |
| + | [[Image:data_longs.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
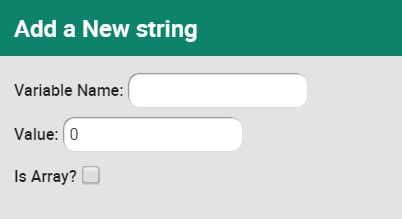
| − | Strings | + | '''Strings''' |
| | | | ||
ASCII or UTF-8 string. Length is unlimited. | ASCII or UTF-8 string. Length is unlimited. | ||
| + | [[Image:data_strings.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Domain | + | '''Domain''' |
| | | | ||
| − | + | Tp, Base or Tool. | |
| + | |||
|} | |} | ||
=I/O Screen = | =I/O Screen = | ||
| − | Allows | + | Allows user to monitor the status of system inputs and outputs, and to toggle outputs. |
IO names are defined in DAT files (TPIN.DAT and TPOUT.DAT). | IO names are defined in DAT files (TPIN.DAT and TPOUT.DAT). | ||
| Line 860: | Line 1,002: | ||
This screen is updated in realtime. | This screen is updated in realtime. | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:IO screen 9.1.jpg|IO screen 9.1.jpg |500px]] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {|border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| + | !width = "100" bgcolor= A5A5A5|'''Setting''' | ||
| + | !width = "350" bgcolor = A5A5A5| '''Description''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Name''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Description''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''State''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Device''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Terminal Screen= | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The Terminal screen is accessible to Admin users only.<br> | ||
| + | Terminal is a command line interface to the softMC. It allows user to send instructions to the drive, and read the drive’s responses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image: terminal screen 10.1.jpg]] | ||
= Diagnostics Screen = | = Diagnostics Screen = | ||
| Line 866: | Line 1,041: | ||
Two views. Devices and Master. | Two views. Devices and Master. | ||
| − | Shows status and properties of the devices and the | + | Shows status and properties of the devices and the Motion-bus in the system. |
[[Image:TP_Diagnostics_motors.png|TP_Diagnostics_motors.png |500px]] | [[Image:TP_Diagnostics_motors.png|TP_Diagnostics_motors.png |500px]] | ||
| Line 876: | Line 1,051: | ||
* Clear Drive Fault – removes all errors from the softMC | * Clear Drive Fault – removes all errors from the softMC | ||
| − | Different icon colors indicate | + | Different icon colors indicate severity of the error. |
* Yellow: Note | * Yellow: Note | ||
* Blue: Info | * Blue: Info | ||
| Line 885: | Line 1,060: | ||
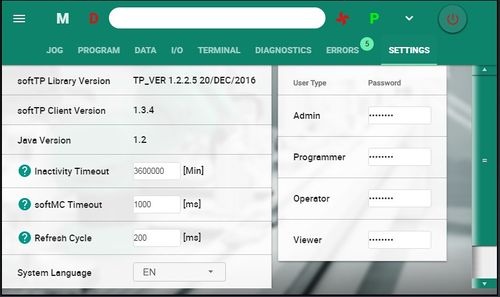
= Settings Screen = | = Settings Screen = | ||
| − | + | For all non-Admin users, shows version information of software components.<br> | |
| + | For Admin level users, also allows setting of passwords, the interface language, and certain system parameters. | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:setting screen 13.1.jpg|setting screen 13.1.jpg |500px]] |
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | ||
| − | |- | + | |-bgcolor = A5A5A5 |
| | | | ||
| − | Setting | + | '''Setting''' |
| | | | ||
| − | Description | + | '''Description''' |
| − | |- | + | |- |
| | | | ||
| − | TP Library Version | + | '''TP Library Version''' |
| | | | ||
Displays the version of the currently loaded set of TP library files. | Displays the version of the currently loaded set of TP library files. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | softTP Client | + | '''softTP Client Version ''' |
| | | | ||
Displays the version of the softTP user interface software. | Displays the version of the softTP user interface software. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Java Version | + | '''Java Version''' |
| | | | ||
Displays the version of the Java software in use. | Displays the version of the Java software in use. | ||
| + | |-bgcolor = A5A5A5 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Inactivity Timeout''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | This is the maximum length of a softTP session without activity, defined in minutes.<br> | ||
| + | Once this time has elapsed, the user must login again. | ||
| + | |-bgcolor = A5A5A5 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''softMC Timeout''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | This is the maximum time for the softTP to wait for a response from the softMC, defined in milliseconds.<br> | ||
| + | Once this time has elapsed, the softTP disconnects from the softMC system. | ||
| + | |- bgcolor = A5A5A5 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Refresh Cycle''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Defines how frequently the softTP retrieves and updates data (e.g., positions of axes), specified in milliseconds. | ||
| + | |-bgcolor = A5A5A5 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''System Language''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Language options for the softTP user interface.<br> | ||
| + | English, Chinese and German are currently available. | ||
| + | |-bgcolor=A5A5A5 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | '''Passwords''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Fields for setting the passwords required for logging in the softTP | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:48, 6 August 2017
| Language: | English • 中文(简体) |
|---|
Contents
Overview
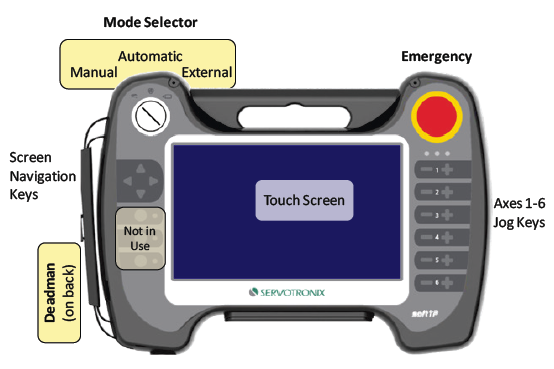
The softTP is a teach pendant (TP) designed for use with softMC 3 and softMC 7 motion controllers and various types of robots, such as SCARA, PUMA and DELTA. The softTP allows operators to move the robot by means of jog keys, and to create and run complete robot programs written in MC-Basic.
The softTP touch screen interface enables quick and easy application development. The softTP software package also includes a full-featured emulator running on Windows/Linux.
Access Permission Levels
The softTP has four different user levels.
- Viewer
- Operator
- Programmer
- Administrator
Each softTP user must login with a password for a specific permission level.
The following table indicates the functions available to each user level.
| Permission Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viewer | Operator | Programmer | Admin | |
|
View main robot data. |
|
|
|
|
|
Switch between TP screens. |
|
|
|
|
|
View the status of digital IOs and error history. |
|
|
|
|
|
Start/stop certain processes (e.g., move?). |
|
|
|
|
|
Start/stop certain programs. |
|
|
|
|
|
View data (variables) but not modify. |
|
|
|
|
|
View programs, but not modify. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acknowledge errors. |
|
|
|
|
|
Enable the robot. |
|
|
|
|
|
Create and edit user programs (UPG/ULB). |
|
|
|
|
|
Create and edit (teach) program variables. |
|
|
|
|
|
Create and edit all types of MC Basic program files (PRG/LIB & UPG/ULB). |
|
|
|
|
|
Change passwords of all user levels. |
|
|
|
|
|
Access the Terminal screen. |
|
|
|
|
This document presents screens as seen by PROGRAMMER.
softTP Switches
Deadman Switch
The deadman switch is located on the back of the softTP. The switch has three positions: released, partially pressed, and fully pressed.
In Manual mode, motion and jogging commands can be issued from the teach pendant only when the deadman switch is in the intermediate, partially-pressed position.
If the deadman switch is released, or fully pressed, while axes are in motion, the motion stops automatically.
Using Emulator
Set in your browser the following address:
http:<ip address>/tp/emulator
where <ip address> is the IP address of your softMC
for example:
http://10.4.20.148:1207/tp/emulator
When using TP Emulator, the deadman switch status is represented by the on‑off vertical switch on the left side of the screen.
Emergency Stop
Pressing the Emergency switch automatically powers off the motors, stops motion and and disables the axes.
If the robot is equipped with brakes, the brakes are activated.
Mode Selector Switch
The Mode Selector switch on the front of softTP has three positions: Manual, Automatic and External.
If the mode setting is switched from Automatic to Manual while a program is running, program execution stops immediately.
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
|
Manual |
Left position. Manual mode is used for jogging the axes. When in Manual mode, the robot velocity is reduced and the user cannot issue run commands or edit programs. |
|
Automatic |
Middle position. Automatic mode is used for editing/running programs. When in Automatic mode, the axes cannot be jogged. |
|
External |
Right position. When in External mode, the softTP does not control the robot. |
When using TP Emulator, the mode switch status is represented by the horizontal switch on the top left of the screen.
Interface Elements
Toolbar
| Toolbar | Description | |
|---|---|---|
|
Logout |
Exits the TP Emulator. | |
|
TP Operation Mode |
Indicates the teach pendant’s current operation control mode, as defined by the mode selector switch. | |
|
Text box |
Message field for system notifications. | |
|
Axes in Motion |
Indicates state of the axes: | |
|
Primary TP |
Indicates that the teach pendant in use is the primary TP, if other TPs are connected. (Not currently implemented) | |
|
Collapse/Expand |
Hides/shows the menu bar, to provide additional screen space for program lines. | |
|
Enable | Disable |
Enables and disables all axes, and indicates the state of the axes. |
Menu Bar
The menu bar provides access to the eight softTP screens.
| Screen | Function |
|---|---|
|
Jog |
Used to select the type of robot, and jog the robot/axes in the user-defined frame. |
|
Program |
Used to create, edit, run and debug MC‑Basic programs. |
|
Data |
Used to create, edit, run and debug MC-Basic programs. |
|
IO |
Used to monitor and switch system digital inputs and outputs. |
|
Terminal |
Allows command line entry of MC Basic commands. Accessible to Administrator-users only. |
|
Diagnostics |
Displays settings and status of configured axes and devices. |
|
Errors |
Displays the log of faults in the softMC motion controller. |
|
Settings |
Displays system software components and versions. |
|
settings |
Allows setting of stystem variables. Accessible to Administrator-users only. |
Jog Keys
When Frame is set to Joint, keys are labeled according to axes: J1, J2, J3, and so on.
When Frame is set to Base, Tool or World, keys are labeled according to Cartesian coordinates: X, X, Z, Yaw, Pitch, Roll.
Domains
Domains serve to separate data from programs, thereby allowing manipulation of program data (variables) without affecting program code.
Every program is associated with a domain. In MC-Basic, domains are implemented by a namespace feature of the MC-Basic language. (Refer to: http://softmc.servotronix.com/wiki/Namespace).
All variables of a given domain are automatically saved to a separate file on the softMC disk after they are created or updated.
The softTP provides three system domains for certain data, which do not have associated program files.
Every project has automatically associated domain of the same name.
TP Domain
TP variables are not assigned to a particular program or project.
They can be used freely as auxiliary variables for debugging and other functions.
Base Domain
Base variables are not assigned to any program and are used to store the base property values used by the selected robot.
It is recommended that variables in this domain use the naming format BASE1, BASE2, and so on.
Tool Domain
Tool variables are not assigned to any program and are used to store the tool property values used by the selected robot.
It is recommended that variables in this domain use the naming format TOOL1, TOOL2, and so on.
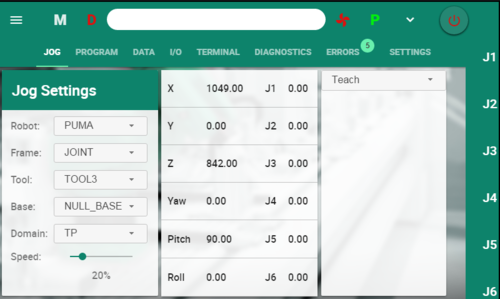
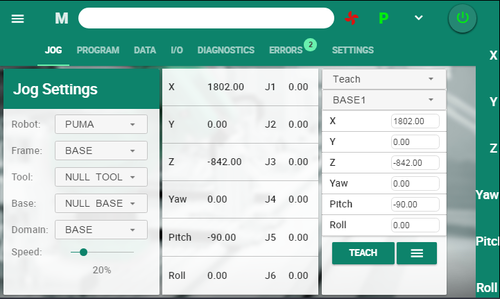
Jog Screen
The Jog screen is the main screen for working with the robot.
- It displays the current robot joint and Cartesian coordinates.
- It enables user to teach/set new points, move(s) to a predefined point.
- It provides tool calibration and align functionality.
Frames
softTP supports five jog frames: Joint, Base, Tool, World XYZ,and World ZYZ.
- Joint frame is used for jogging the individual robot axes: J1 … J6.
- Base, Tool and World frames represent Cartesian frames. When one of these frames is selected, jogging is in XYZ coordinates and in the corresponding orientation axes:
- Base and Tool frames allow jogging of X, Y, Z, Yaw, Pitch and Roll.
- Note that the default Euler-Angle representation of Yaw-Pitch-Roll is a ZYZ rotation sequence only.
- World frame has two modes: ZYZ and XYZ.
- ZYZ is the default mode; it has standard orientation angles as Yaw-Pitch-Roll of a ZYZ rotation sequence.
- XYZ is an alternative mode; it has non-standard orientation angles as Rx-Ry-Rz of an XYZ rotation sequence.
- In MC-Basic, Base, Tool and World frames are considered location data types.
A Cartesian robot frame (for PUMA robot) is a 6-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system in which the robot tool tip position and orientation are defined.
For a PUMA robot both Base and Rtool frames are in the form X-Y-Z-Yaw-Pitch-Roll.
The Frame option in the Jog screen allows you to select a different frame for jogging in. You can set different frame parameters (values) in various ways; for example:
- By using Teach option to teach them directly – this is commonly done for Base.
- By using Tool Calibration options – this is commonly done for Tool.
Teaching Points
Positions are taught in the Jog screen, and defined in either Joint or Cartesian coordinates.
Before teaching a point, you must first create a Location or a Joints position in the Data screen. Be sure the position is attached to the appropriate Domain.
In the Jog screen, make sure Domain and Frame are set accordingly.
Use the Teach button to set position coordinates automatically, or enter position values manually.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
Robot |
The specific type of robot or axis for movement or position teaching. |
|
Frame |
Cartesian (Tool, Base and World): Linear movement along X, Y and Z directions, angular motion around a static XYZ coordinate. |
|
Tool |
Used for selecting the actual tool:
|
|
Base |
Used for selecting the actual base:
|
|
Domain |
Used for selecting the domain:
|
|
Speed |
Slider to increase/decrease the jogging speed, as a percentage of the maximum speed. |
|
X Y Z Yaw (Rx) Pitch (Ry) Roll (Rz) |
Displays the Cartesian coordinates of the robot even when operating in Joint mode. |
|
Teach |
Used to define the values (Joint or Cartesian) to be taught. Enter position values manually, or press Teach. |
|
Move |
Generates joint interpolated motion to the specified target |
|
Moves |
Generates Cartesian interpolated motion (straight line) to the specified target. |
|
Tool Align |
Aligns the Tool X, Y or Z direction with the nearest World axis, while the tool tip remains in position |
|
Tool Calibrate |
Two methods for calibrating the tool:
|
Program Screen
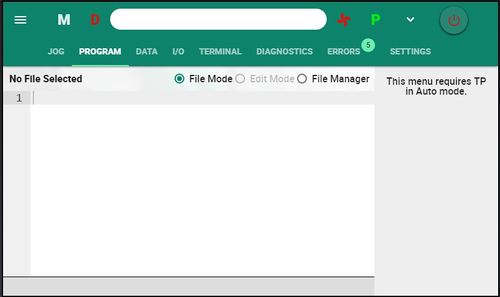
The Program screen is used for creating, editing, running and debugging MC‑Basic programs.
The file extensions *.UPG user programs and *.ULB for user libraries are used to distinguish user programs from general system programs and settings.
Administrator level users can access and manipulate both global (*.PRG/*.LIB) and user (*.UPG/*.ULB) programs and libraries.
Programmer level users can create/edit/run/debug user programs only (*.UPG) and user libraries only (*.ULB).
Projects created by programmer level users generate four files:
| name.UPG |
The main user task. |
|---|---|
| name.ULB |
The library containing the functions and subroutines used in the main user task. |
| name.DEF |
The declarations of all domain variables. (not visible by the user) |
| name.VAR |
The currently defined values of the domain variables. (not visible by the user) |
A project is set of files with same names but different extension (e.g. TASK.UPG, TASK.ULB, TASK.DEF and TASK.VAR.) Non-Admin users only see files with the extensions UPG and ULB.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
Project (File) Mode |
PROGRAMMER |
|
Open Project |
Opens an existing project. |
|
New Project |
Opens a new project. |
|
File Mode |
ADMINISTRATOR |
|
Open File |
Opens an existing file. |
|
New File |
Open a new file. |
|
Load |
Loads a program and associated library from the softMC flash memory to the softMC RAM so that the program can be executed. |
|
Unload |
Unloads a program/library from the softMC RAM so that they can be edited. |
|
Kill |
Aborts execution of a running program. |
|
Idle |
Stops the program at the end of the line currently being executed. |
|
Run |
Starts execution of the program. |
|
Jump to Line |
Jump to a line in current program. |
|
Step Over |
Skip over the subroutine. |
|
Step Into |
Step into the subroutine. |
|
Step Out |
Exit the subroutine. |
|
Edit Mode |
Provides the code syntax for commonly used instructions, including prompts for the data required for completing the code line/s. |
|
Program |
Instructions for defining subroutines and functions.
|
|
Flow Commands |
Instructions used to change the flow of a program based on specific conditions.
|
|
Interpolation |
|
|
Motion Commands |
|
|
I/O |
|
|
Project Manager |
PROGRAMMER |
|
File Manager |
ADMINISTRATOR |
|
[Project/File list] |
|
|
Delete |
Deletes selected project. |
|
Save As |
saves a copy of current project using a new name. |
|
Rename |
Rename the current project. |
Data Screen
The Data screen is used for creating and editing variables in the domain that is currently selected.
Variables can be robot positions or any other data type that is supported in MC‑Basic, such as long, double and string.
Select the domain, and the type of variable, then click the + button to create a variable.
A dialog box opens according to type of variable.
Enter values.
|
Setting |
Description |
|
Locations |
World/Cartesian positions. |
|
Joints |
|
|
Longs |
|
|
Doubles |
|
|
Strings |
|
|
Domain |
Tp, Base or Tool. |
I/O Screen
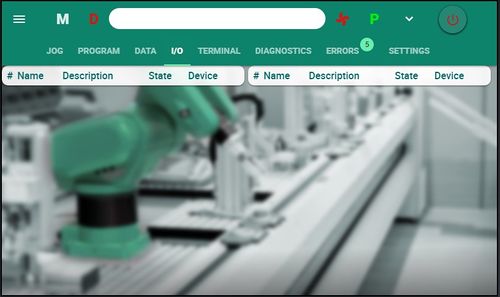
Allows user to monitor the status of system inputs and outputs, and to toggle outputs.
IO names are defined in DAT files (TPIN.DAT and TPOUT.DAT).
This screen is updated in realtime.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
|
|
Description |
|
|
State |
|
|
Device |
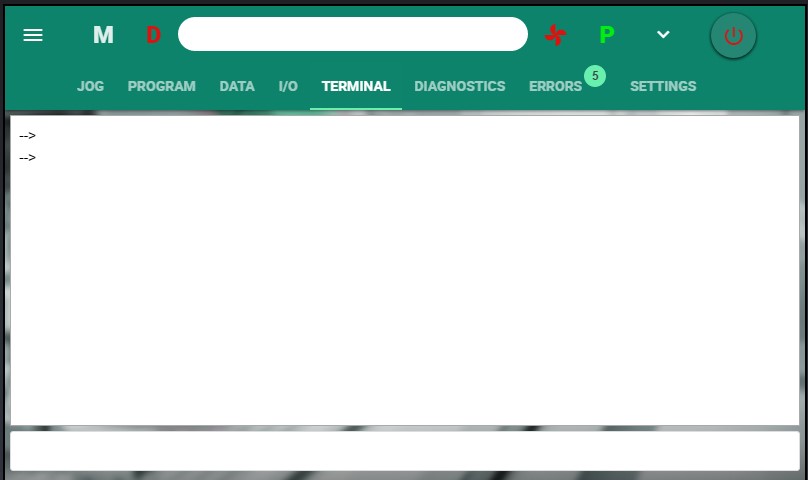
Terminal Screen
The Terminal screen is accessible to Admin users only.
Terminal is a command line interface to the softMC. It allows user to send instructions to the drive, and read the drive’s responses.
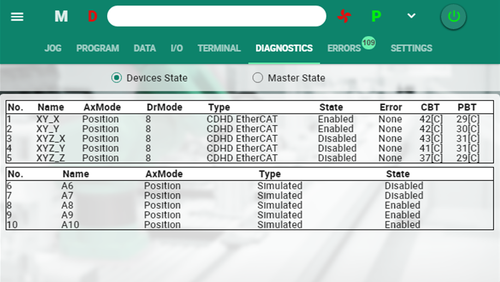
Diagnostics Screen
Two views. Devices and Master.
Shows status and properties of the devices and the Motion-bus in the system.
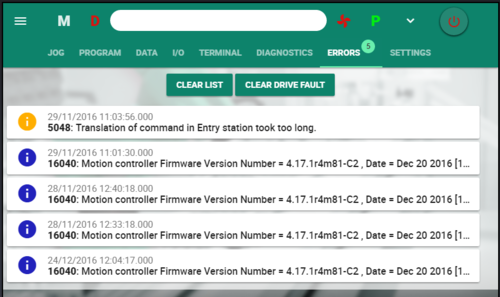
Errors Screen
When errors occur, an icon is displayed in the menu bar, and indicates the total number of errors.
- Clear List – removes all errors from the list
- Clear Drive Fault – removes all errors from the softMC
Different icon colors indicate severity of the error.
- Yellow: Note
- Blue: Info
- Red: Error
Settings Screen
For all non-Admin users, shows version information of software components.
For Admin level users, also allows setting of passwords, the interface language, and certain system parameters.
|
Setting |
Description |
|
TP Library Version |
Displays the version of the currently loaded set of TP library files. |
|
softTP Client Version |
Displays the version of the softTP user interface software. |
|
Java Version |
Displays the version of the Java software in use. |
|
Inactivity Timeout |
This is the maximum length of a softTP session without activity, defined in minutes. |
|
softMC Timeout |
This is the maximum time for the softTP to wait for a response from the softMC, defined in milliseconds. |
|
Refresh Cycle |
Defines how frequently the softTP retrieves and updates data (e.g., positions of axes), specified in milliseconds. |
|
System Language |
Language options for the softTP user interface. |
|
Passwords |
Fields for setting the passwords required for logging in the softTP |