Difference between revisions of "Modbus Communication API"
(Created page - Draft: 1) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 13:49, 12 April 2016
Contents
Overview
Basic Overview
This describes how to set up Modbus communication for the softMC, and how to generate softMC scripts to handle Modbus communication. It is assumed you are familiar with the principles of Modbus communication, although some of them will be described in this page. It is also assumed your are familiar with the softMC, ControlStudio and MC-Basic programming.
Modbus Communication Background
- A Motion Controller (MC) can act as a server (slave), a client (master) or both at the same time.
- Each MC connection (TCP/RTU) can be used either as a server component (if the connection is used by the MC’s server-side) or as a client component (if the connection is used by the MC’s client-side).
- Each component has its own parameters that defines it.
- When the MC acts as a server, all server components share the same memory address space, thus acting as 1 server with multiple connections.
- Each server (slave) on a Modbus network has its own deviceID, which is a number between 1 and 247.
The Modbus server registers
- The types of registers in the Modbus Server address space include the following:
- Bits (1-bit registers)
- Input Bits (1-bit READ-ONLY registers)
- Holding Registers (16-bit registers)
- Input Registers (16-bit READ-ONLY registers)
- Servers can read and write their own address space.
- Clients can read and write a remote server’s address space.
Getting Started
In order to get started in using the Modbus features:
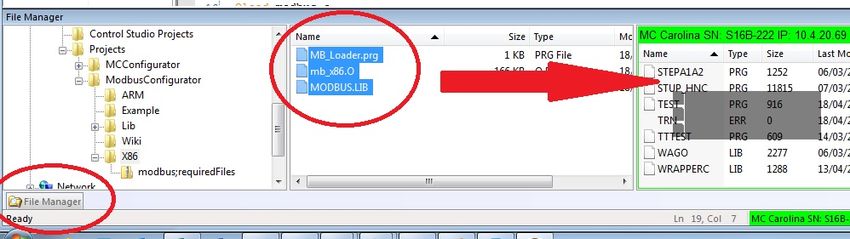
- Using the ControlStudio File Manager, Upload the following files to your MC:
- mb_x86.O (for X86 Systems) / mb_armA9.O (for ARM Systems)
- Modbus.lib
- Load the files to memory, by typing (in the Terminal):
- Oload mb_x86.O
- loadglobal Modbus.lib
Initializing a Modbus Server
- To initialize the Modbus server address space, call:
- ?init_multi_server([bits],[input_bits],[holding registers],[input_registers])
- The function prints "success" and returns 0 on success, or return an error code on failure.
- Notice:
- This is NOT required when softMC does not run a modbus server.
- You can call this method only if no servers are running.
Server Components
Adding server components
- Each time you'll add a component, you will receive a handle, which is the component's identifier (for later use).
- It is best to keep this handles in variables inside your program.
Creating a TCP server component
handle = mb_tcp_server_create([port],[deviceID])
- This opens a TCP connection to the server on port [port] with deviceID [deviceID], and starts the created server immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, or an error code on failure.
Creating an RTU server component
handle = mb_rtu_server_create([type],[port],[baudrate],[data bits],[stop bits],[parity],[deviceID])
- This opens an RTU connection with the given parameters, and starts the created server immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, or an error code on failure.
Stopping Server Components
Stopping a specific server component
You can stop a specific server component by passing its handle to:
result = mb_server_stop([handle])
- Given a handle, this will stop and free the memory of the appropriate server component.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Stopping all server components
You can stop all server components with a single call to:
result = mb_server_stop_all
This function will:
- Stop and free all server components.
- Free the shared address space.
- Return 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Client Components
Adding client components
- Each time you'll add a component, you will receive a handle, which is the component's identifier (for later use).
- It is best to keep this handles in variables inside your program.
Adding a TCP Client component
handle = mb_tcp_client_create([ip],[port])
- This will opens a TCP connection to the client on the given ip and port, and start the client immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, -1 on failure.
Adding an RTU Client component
handle = mb_rtu_client_create([type],[port],[baudrate],[data bits],[stop bits],[parity])
- This will open an RTU connection to the client with the given parameters, and start the client immediately.
- Returns a handle on success, -1 on failure.
Stopping client components
A specific client can be stopped by calling:
result = mb_client_stop([handle])
- Given a handle, this will stop and free the memory of the appropriate client component.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Reset the Modbus System
Sometimes, a user may wish to stop all server and client components at once, and reset the Modbus system (for example, when a user want to initialize a different Modbus system). To do that, call:
result = mb_reset
This function:
- Stops all running servers and clients.
- Frees their memory.
- Frees the shared address space.
- Reset the handle counter.
- Returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
Reading and Writing
- Servers can read and write their own address space.
- Clients can read and write a remote server’s address space.
- Therefore, Servers and clients use different functions to read/write data from the address space.
Server Components
Reading
Reading from Holding registers
Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_LONG(…) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_SHORT(…) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_FLOAT(…) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_REG_DOUBLE(…)
Reading from Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_READ_BIT([addr])
Reading from Input registers
Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_LONG(…) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_SHORT(…) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_FLOAT(…) Val = MB_SERVER_READ_INREG_DOUBLE(…)
Reading from Input Bits registers
val = MB_SERVER_READ_INBIT([addr])